A team of researchers from Google Research and UC Santa Cruz released DeepSomatic, an AI model that identifies cancer cell genetic variants. In research with Children’s Mercy, it found 10 variants in pediatric leukemia cells missed by other tools. DeepSomatic has a somatic small variant caller for cancer genomes that works across Illumina short reads, PacBio HiFi long reads, and Oxford Nanopore long reads. The method extends DeepVariant, detects single nucleotide variants and small insertions and deletions in whole genome and whole exome data, and supports tumor normal and tumor only workflows, including FFPE models.
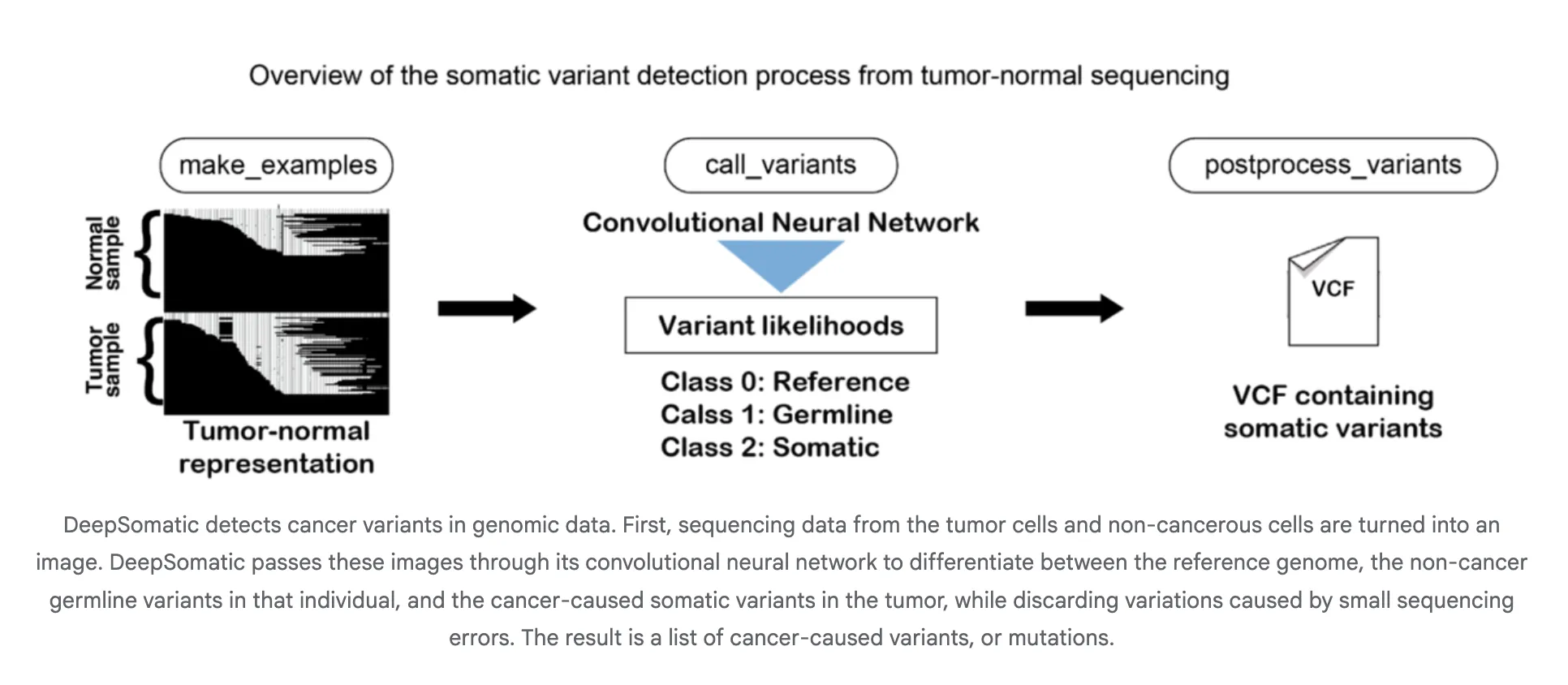
How It Works?
DeepSomatic converts aligned reads into image like tensors that encode pileups, base qualities, and alignment context. A convolutional neural network classifies candidate sites as somatic or not and the pipeline emits VCF or gVCF. This design is platform agnostic because the tensor summarizes local haplotype and error patterns across technologies. Google researchers describe the approach and its focus on distinguishing inherited and acquired variants including difficult samples such as glioblastoma and pediatric leukemia.
Datasets and Benchmarking
Training and evaluation use CASTLE, Cancer Standards Long read Evaluation. CASTLE contains 6 matched tumor and normal cell line pairs that were whole genome sequenced on Illumina, PacBio HiFi, and Oxford Nanopore. The research team releases benchmark sets and accessions for reuse. This fills a gap in multi technology somatic training and testing resources.
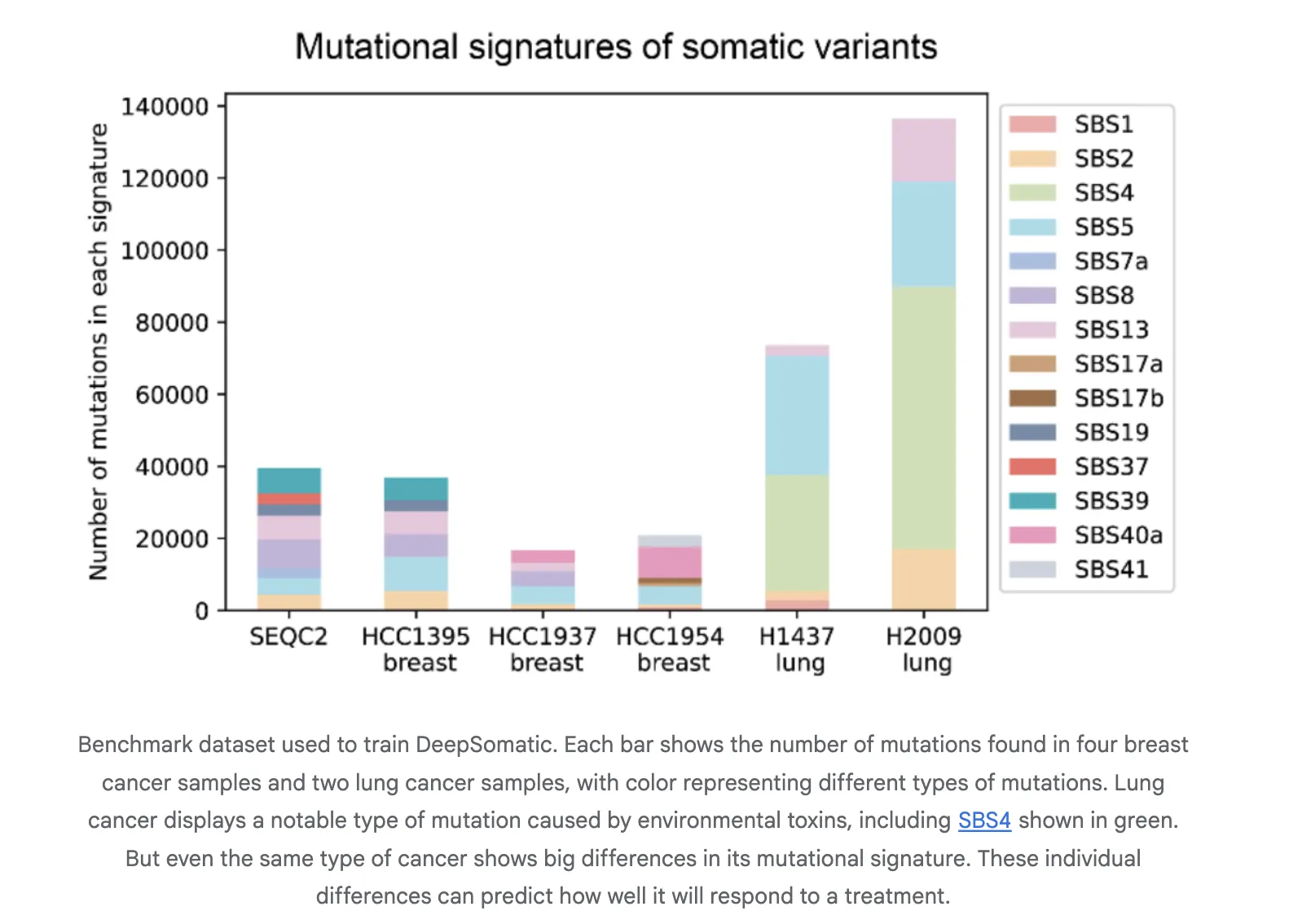
Reported Results
The research team report consistent gains over widely used methods in both single nucleotide variants and indels. On Illumina indels, the next best method is about 80 percent F1, DeepSomatic is about 90 percent. On PacBio indels, the next best method is under 50 percent, DeepSomatic is above 80 percent. Baselines include SomaticSniper, MuTect2, and Strelka2 for short reads and ClairS for long reads. The study reports 329,011 somatic variants across the reference lines and an additional preserved sample. Google research team reports that DeepSomatic outperforms current methods with particular strength on indels.
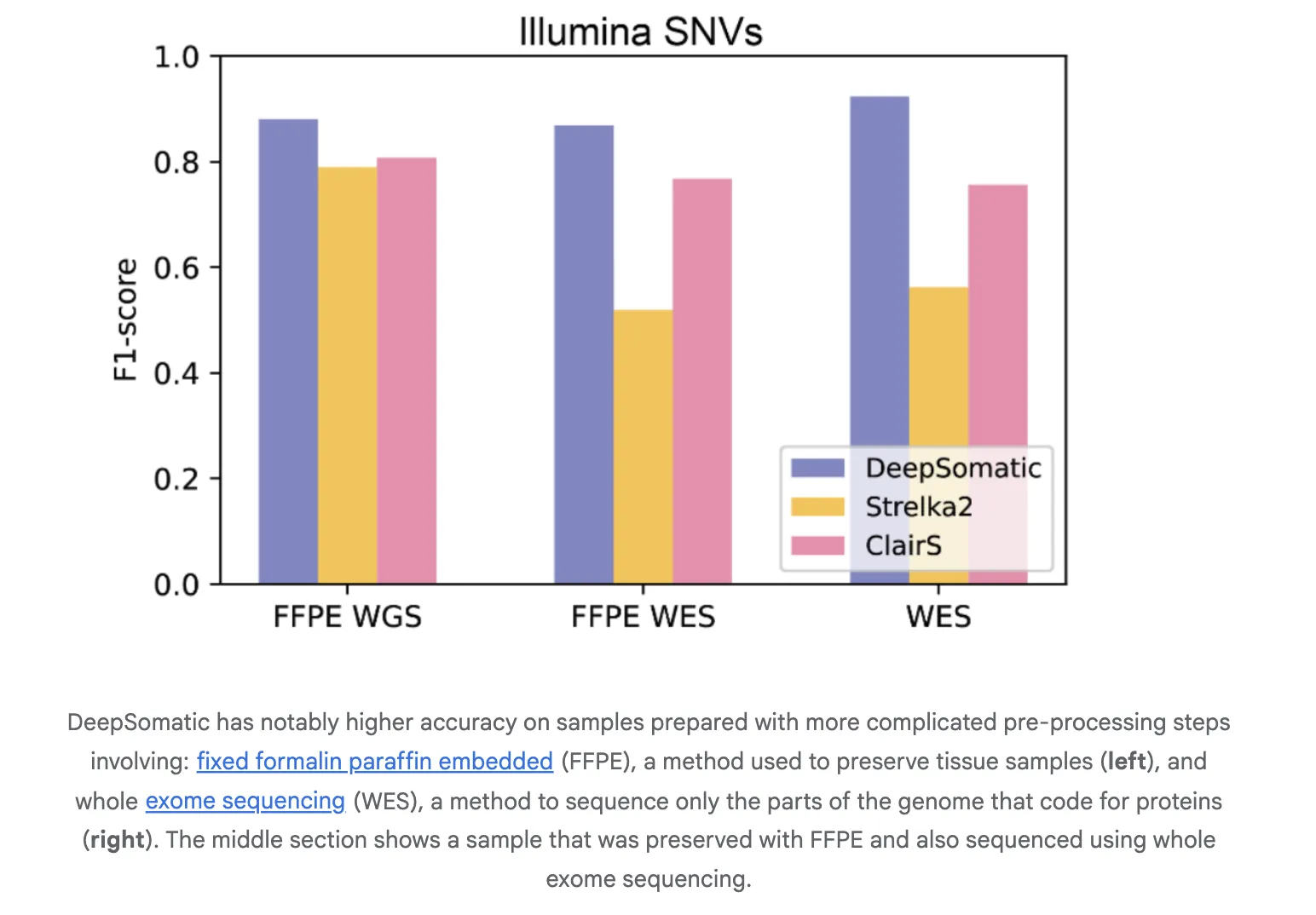
Generalization to Real Samples
The research team evaluates transfer to cancers beyond the training set. A glioblastoma sample shows recovery of known drivers. Pediatric leukemia samples test the tumor only mode where a clean normal is not available. The tool recovers known calls and reports additional variants in that cohort. These studies indicate the representation and training scheme generalize to new disease contexts and to settings without matched normals.
Key Takeaways
- DeepSomatic detects somatic SNVs (single nucleotide variants) and indels across Illumina, PacBio HiFi, and Oxford Nanopore, and builds on the DeepVariant methodology.The pipeline supports tumor normal and tumor only workflows, includes FFPE WGS and WES models, and is released on GitHub.It encodes read pileups as image like tensors and uses a convolutional neural network to classify somatic sites and emit VCF or gVCF. Training and evaluation use the CASTLE dataset with 6 matched tumor normal cell line pairs sequenced on three platforms, with benchmarks and accessions provided.Reported results show about 90 percent indel F1 on Illumina and above 80 percent on PacBio, outperforming common baselines, with 329,011 somatic variants identified across reference samples.
Editorial Comments
DeepSomatic is a pragmatic step for somatic variant calling across sequencing platforms, the model keeps DeepVariant’s image tensor representation and a convolutional neural network, so the same architecture scales from Illumina to PacBio HiFi to Oxford Nanopore with consistent preprocessing and outputs. The CASTLE dataset is the right move, it supplies matched tumor and normal cell lines across 3 technologies, which strengthens training and benchmarking and aids reproducibility. Reported results emphasize indel accuracy, about 90% F1 on Illumina and more than 80% on PacBio against lower baselines, which addresses a long running weakness in indel detection. The pipeline supports WGS and WES, tumor normal and tumor only, and FFPE, which matches real laboratory constraints.
Check out the Technical Paper, Technical details, Dataset and GitHub Repo. Feel free to check out our GitHub Page for Tutorials, Codes and Notebooks. Also, feel free to follow us on Twitter and don’t forget to join our 100k+ ML SubReddit and Subscribe to our Newsletter. Wait! are you on telegram? now you can join us on telegram as well.
The post Google AI Research Releases DeepSomatic: A New AI Model that Identifies Cancer Cell Genetic Variants appeared first on MarkTechPost.

