Author: Aqsa Taylor
Co-author: Francis Odum
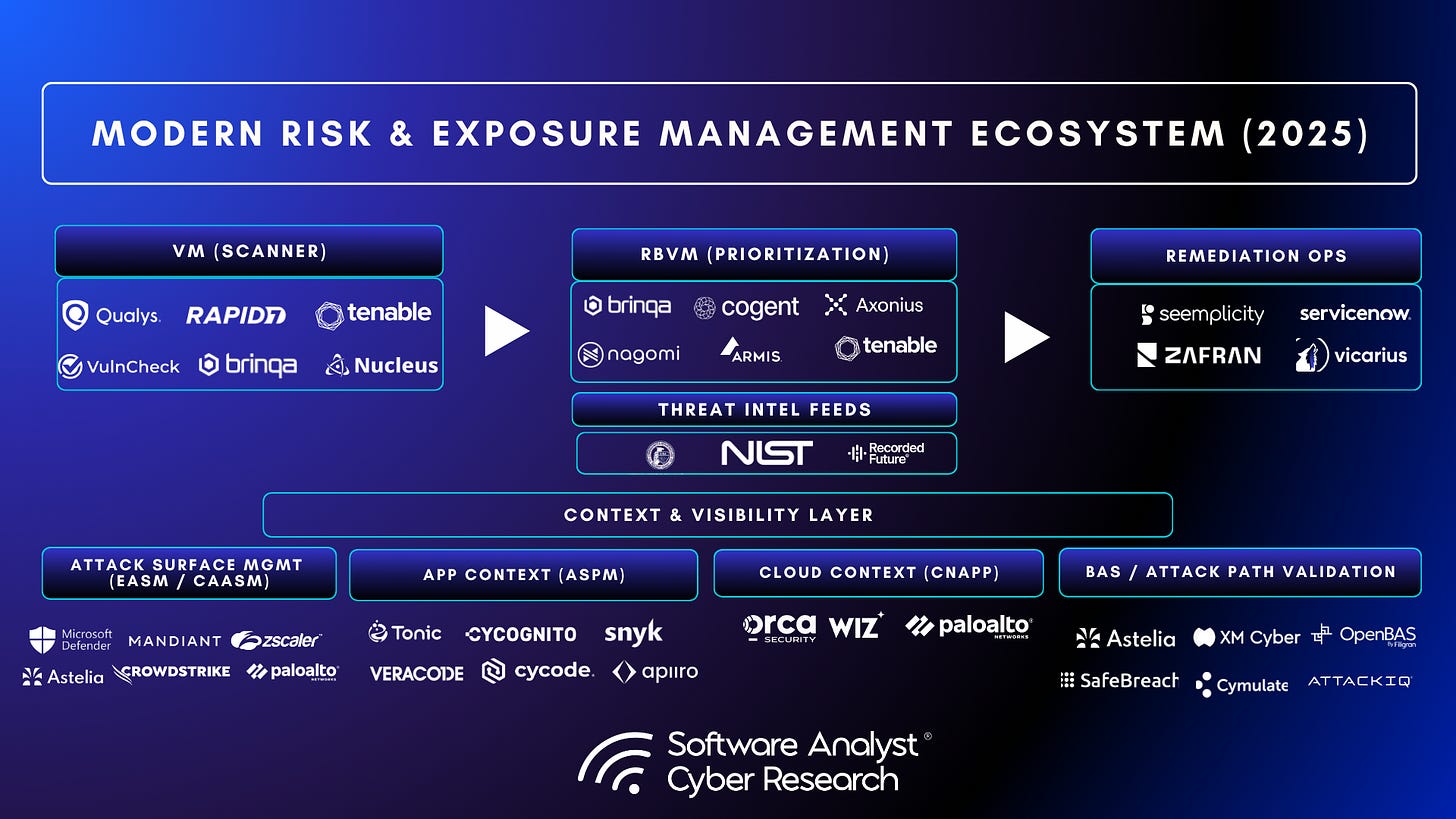
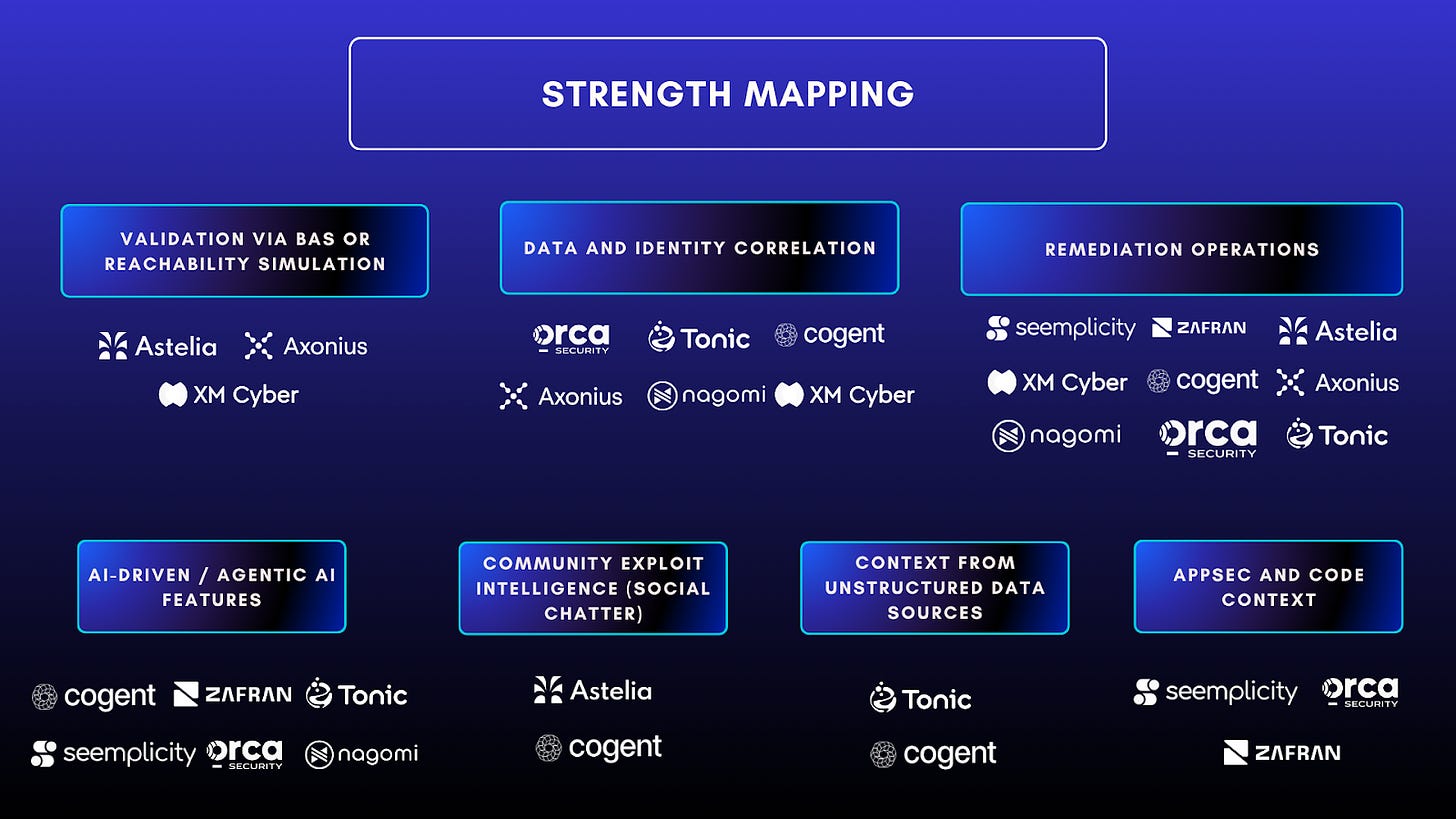
Disclaimer: The purpose of this image is to provide a high-level depiction of various risk and exposure management categories, and it is not intended to rank the vendors (many of them cross categories in capabilities). It is also not all-inclusive, but rather based on the vendors we have interacted with in some capacity.
Introduction
Vulnerability management is not what it was in the 2000s. Factors like CVSS scores, vulnerability counts, and the number of resolved CVEs are no longer the primary standards. Today, organizations do not need reminders to scan their resources for vulnerabilities because most already do so. The main struggle now is prioritization: knowing what truly matters, understanding the impact of not fixing it, and showing how to quickly address it.
In 2025, the combination of faster attacker breakout times, the use of AI to scale exploits, expanding attack surfaces, and increased board-level scrutiny and liability for CISOs has made exposure management a top organizational priority. As a result, the traditional ways of defining exposure or risk and calculating the probability of exploit have been evolving.
Practitioners are asking deeper questions to justify risk scores, the what, why, and how: what factors constitute an evolved definition of “exposure,” why this matters to their organization, and how to remediate this risk to deliver measurable outcomes to the board.
The market has responded accordingly. Vendors are quickly converging categories: Vulnerability Management (VM), Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM), Attack Surface Management (ASM), Cyber Asset Attack Surface Management (CAASM), Application Security Posture Management (ASPM), and Breach and Attack Simulation (BAS). These capabilities, under the CTEM umbrella, are now integrated within modern risk and exposure management platforms.
To bring key insights into this market, we conducted a deep dive into the world of risk prioritization and exposure management. We interviewed practitioners and security leaders from both large and small organizations to understand their primary concerns around risk and exposure. We also analyzed vendors that categorize themselves under the CTEM umbrella to assess how they have evolved in addressing practitioner concerns.
The goal of this report is to articulate practitioner concerns, assess how leading vendors are addressing them, present unbiased findings from platform deep dives, in-depth questionnaires, and customer interviews, and produce a practical framework for organizations looking to operationalize risk management.
This report highlights the major trends shaping exposure management in 2025 and their impact on security teams. We examine how exposure programs deliver value today, where they must evolve, and the characteristics that distinguish modern platforms. The analysis focuses on vendor convergence across VM, ASM, CAASM, and CNAPP, the shift toward exploitability and runtime-driven prioritization, and the growing role of automation and AI in defining Modern Risk and Exposure Management Platforms.
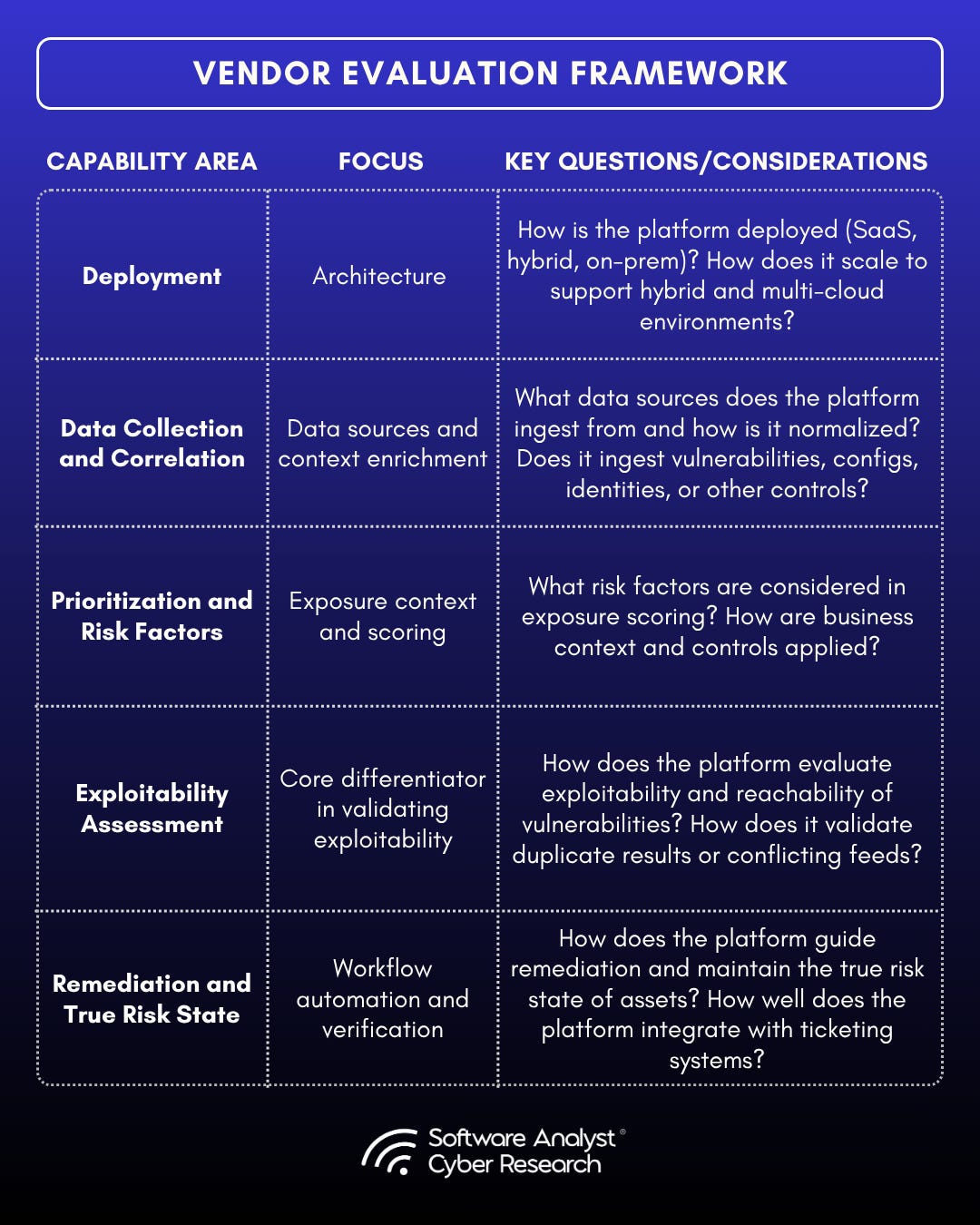
To maintain vendor neutrality, we examined practitioner perspectives, vendor strategies, customer references, and independent market research. To ground these concepts in practical assessment, we evaluated vendors using our DDPER (Deployment, Data Collection, Prioritization, Exposure, Remediation) framework.
The report also provides a step-by-step practitioner guide to selecting the best risk and exposure management solution for organizational needs. It is designed to separate utility from hype and provide security leaders with a clear framework for evaluating exposure and risk in their environments.
Actionable Insights
Risk and Exposure Management is being redefined
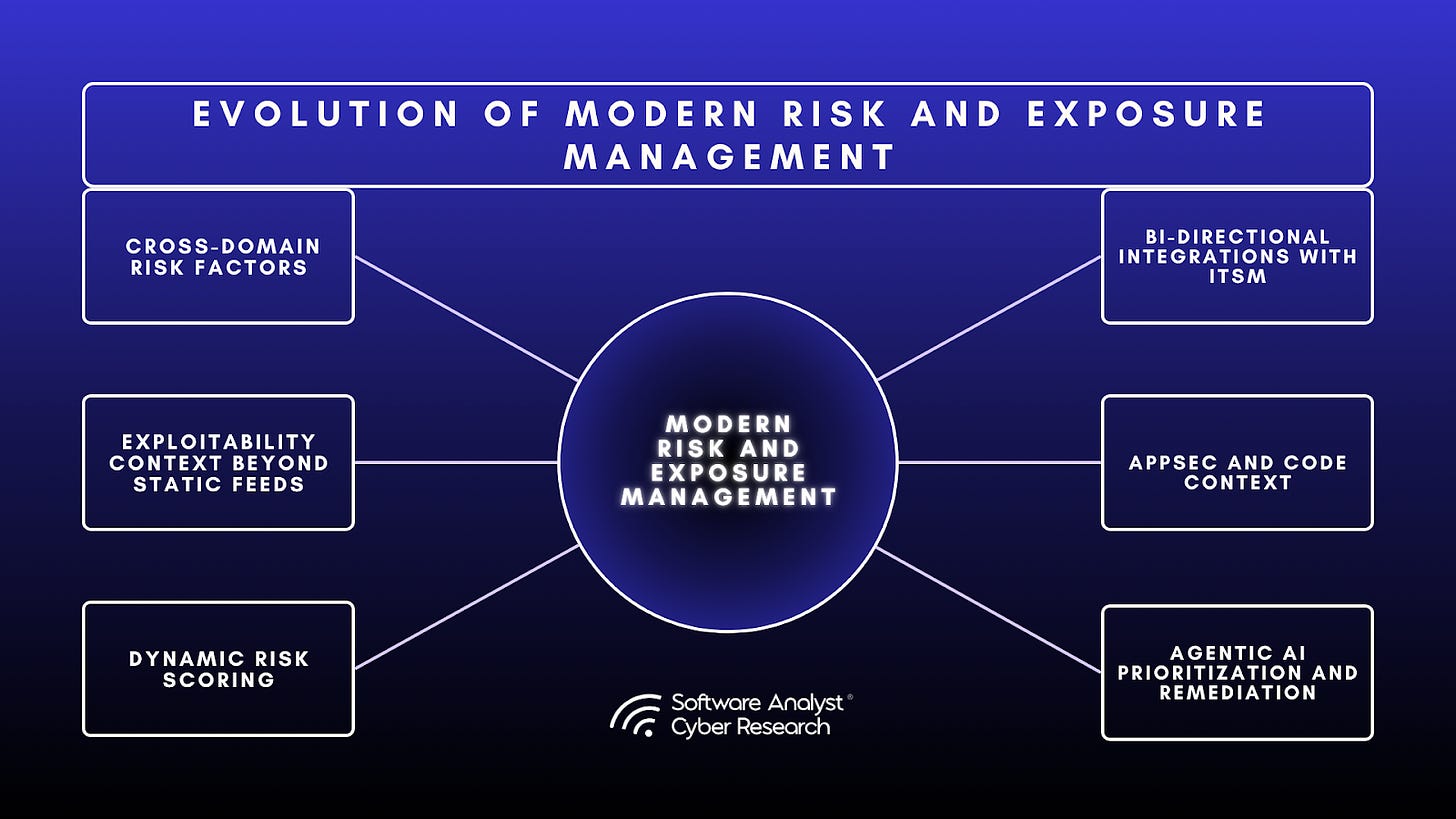
Modern exposure platforms are challenging how exposure was calculated in the past by moving past configuration reads and performing true network reachability, ingesting context from unstructured data sources and even looking at social chatter for probability of exploitation beyond KEV and EPSS databases.
AI and automation are maturing into core utilities:
AI agents are shifting from hype to function, assisting with ownership mapping, remediation orchestration, and contextual analysis to reduce operational overhead and mean time to remediation (MTTR).
Capability convergence is accelerating:
VM, RBVM, ASM, CAASM, ASPM, BAS, CTEM and CNAPP are merging into unified Risk and Exposure Management platforms, providing dynamic scoring, context driven exposure reduction loops.
Aggregator style platforms are rising
Aggregator-style exposure management platforms focus on consolidating data from multiple scanners, posture tools, and threat feeds into a single normalized risk view. They excel in organizations with mature, diverse toolsets.
Pure scanning platforms prioritize depth and native visibility
Pure scanning or unified platforms perform their own continuous scanning across cloud, infrastructure, identity, and application layers. They offer immediate visibility and control, eliminating dependency on external data sources.
Remediation operations bridge security and IT
Leading platforms now include bi directional ticketing, fix aggregation, SLA tracking, and automated verification to ensure findings translate into measurable risk reduction.
Board reporting is outcome based, not activity based
Success metrics now track risk reduction, exposure trends, and exploitability validation, not the number of vulnerabilities fixed or scans completed.
Market divergence is emerging
Platforms are evolving into two broader categories, aggregators that unify multi tool data for contextual prioritization, and in-house scanning platforms that integrate scanning, analytics, and automated remediation in-house.
Practical guide to selecting the right solution
The Practitioner’s Guide helps organizations choose and implement the right exposure management solution by outlining a clear, step-by-step framework to assess needs and then rank vendors against those needs to pick the right solution.
SACR Prediction
Aggregator platforms are adding lightweight in-house scanning to reduce reliance on external tools and offer a single source of truth. Meanwhile, pure-play scanners are expanding into contextual analytics and automated remediation. Both are converging toward autonomous, outcome-driven exposure management focused on measurable risk reduction.
Quick Recap on Industry Definitions
Taken together, these challenges show why vulnerability management has had to evolve. The industry’s definitions have shifted over time as well: from traditional Vulnerability Management to Risk-Based approaches, to more unified pipelines, to Continuous Threat Exposure Management. Before outlining the priorities security leaders are setting for 2025, it is important to establish this progression and align on the definitions of the different models in the vulnerability management world.
VM (Vulnerability Management)
This is the basic foundation. It includes a program for scanning all assets for vulnerabilities and providing a list of vulnerabilities with priorities that are based on CVSS scores. This does not take any other environmental factors into account.
Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM)
An evolution of VM that integrates “risk” to prioritize remediation. Key inputs include exploit intelligence from databases such as the Known Exploited Vulnerabilities (KEV) catalog, which identifies what is being exploited now, and the Exploit Prediction Scoring System (EPSS), which identifies what is likely to be exploited soon.
Unified Vulnerability Management (UVM)
A consolidated approach to vulnerability management that ingests vulnerability findings from multiple sources, normalizes and deduplicates them and helps with prioritization based on centralized view.
Attack Surface Management (ASM)
It maps every internet-facing asset and service, ties each one back to its owner, and calls out exposures like open ports, misconfigurations, leaked credentials, or expired certificates. The goal isn’t just visibility, it’s also validation. When combined with Breach and Attack Simulation (BAS), security teams can understand which exposures are truly exploitable.
Application Security Posture Management (ASPM)
ASPM gathers data from every part of the application lifecycle, including SAST, DAST, SCA, secrets management, IaC, supply chain, cloud configurations, and runtime environments, to give teams a unified view of risk. But it is not just about visibility. ASPM adds asset posture context, clarifies ownership, and connects with existing workflows.
Continuous Threat Exposure Management (CTEM)
A term defined by Gartner for a program defined with continuous identification, validation, prioritization, and reduction of exposures across the enterprise attack surface. Emphasizes ongoing discovery, business context, attack-path validation, and measurable reduction of exposure.
Evolution of Vulnerability Management into Exposure Management
Vulnerability management used to mean running periodic scans that generated long lists of issues, with severity ranked mainly by CVSS scores. That approach no longer fits. The modern cloud-native applications, dynamic infrastructure, and a constantly shifting threat landscape has changed expectations. What organizations want are solutions that move beyond static feeds and config reads, providing prioritization that reflects real exploitability and business context, platforms under the CTEM umbrella are evolving to address these needs, thus leading to the evolution of Modern Risk and Exposure Management Platforms.
Factors that led to Modernization
Before diving into the key characteristics of modern risk and exposure management platforms, it’s important to understand the factors that led to the evolution of vulnerability management into broader and more advanced exposure management platforms. Understanding these gives you the lens through which to judge what “modern” really means in 2025.
Noise and Alert Fatigue: From Detection Overload to Decision Overload
Most traditional vulnerability tools still behave like finding lists, not risk reducers. They provide good insights on the vulnerabilities discovered, maybe even provide context on exploit based on KEV or EPSS feeds but less details in terms of active risk pertaining to that specific customer’s environment. The result is alert fatigue, missed SLAs, and growing backlogs that neither reflect true risk nor move remediation forward in a measurable way.
Shallow Prioritization and Context Gaps: Fixing What’s Visible, Missing What’s Critical
In legacy vulnerability platforms, risk ranking often leans on external signals (CVSS scores, EPSS, KEV) without factoring in internal context like network exposure, identity privileges, runtime state, or asset criticality. This drives mis-prioritization, where teams spend cycles fixing non-exploitable issues while missing real attack paths. Not having exploitability or reachability analysis leaves security teams with a long list of vulnerability issues with misaligned priorities.
Activity Over Outcomes: Doing More, Achieving Less
Dashboards that highlight the number of CVEs fixed rather than actual risk reduction create a false sense of progress. Activity metrics are not risk metrics. Without environment-aware prioritization, workflows optimize for throughput instead of impact, widening the gap between security teams focused on reducing exposure and engineering teams measured on delivery, not ticket counts.
Data Integrity and Trust Challenges: Proving More, Fixing Less
Conflicting feeds, backports, and false positives can waste time that should be spent accurately remediating risks. Discovering more vulnerabilities is no longer an automatic proof of a better scanner, as false positives often consume more practitioner time to resolve than addressing actual risk. Practitioners want platforms that reduce false positives and duplicates to improve trust and the accuracy of risk assessment.
Introducing Modern Risk and Exposure Management Platforms
There are several key ways we see vulnerability risk and exposure management being redefined in 2025, driven by practitioner concerns, pro-active security modeling, fast-paced threat landscape and introduction of AI from hype to utility. Modern risk exposure management platforms transform past approaches to defining exposure with exploit context derived beyond static configuration reads, true network reachability analysis via simulations, probability of exploit beyond static feeds like EPSS and KEV, social intelligence derived from internet chatter, bi-directional integrations with ticketing platforms to reduce stale risk states and AI-assisted prioritization and remediation. They unify asset intelligence, threat context, business data, and automation to measure, explain, and act on real risk. Here are some new trends related to how vendors are approaching vulnerability risk and exposure management in 2025 -
Control Optimization to Contextual Exposure Modeling
Modern platforms incorporate runtime verification, network reachability, exploit intelligence, presence of compensating controls and business context to measure true exploitability rather than just relying on exposure presence via asset configuration.
Unstructured Data Sources
We are also seeing an emergence of analyzing unstructured data sources to gain additional context about the business criticality of an asset based on information from sources such as ITSM and ticketing systems, collaboration platforms like slack, knowledge repositories and dev tools.
Exploitability Beyond Feeds
Some modern platforms are looking beyond exploitability databases like KEV and EPSS, using social, community, and open-source chatter to detect exploit trends early, feeding those signals into exploitability scoring and contextual risk models
Focus on Remediation
Modern platforms are turning AI from hype to utility by using AI agents for decision automation to perform correlation, ownership resolution, and remediation orchestration. There is still some hesitancy on how much AI should be involved in this process, however clients of these vendors have shared positive feedback.
AppSec and Code Context
Modern platforms are shifting from infrastructure-centric vulnerability scanning to unified exposure management that connects code, cloud, and runtime layers in a single risk model. By integrating application-security signals from SAST, DAST, SCA, and code repositories with contextual and runtime data, they link vulnerabilities in production back to their source. This convergence is turning exposure management into a code-to-cloud discipline, aligning exploitability insights, developer ownership, and remediation workflows within one continuous loop for proactive security.
Process Graphs
Attack paths are becoming common, but we are seeing a rising trend of visualizing business process graphs combined with exposure context.
Key Trends in Risk and Exposure Management in 2025
We interviewed practitioners and asked them about their priorities in this evolving vulnerability management scope and what pain points they would really like to see addressed. We then mapped these against the practical ways vendors are solving these concerns to give you insights on the key trends on Risk and Exposure Management platforms.
Risk vs Coverage
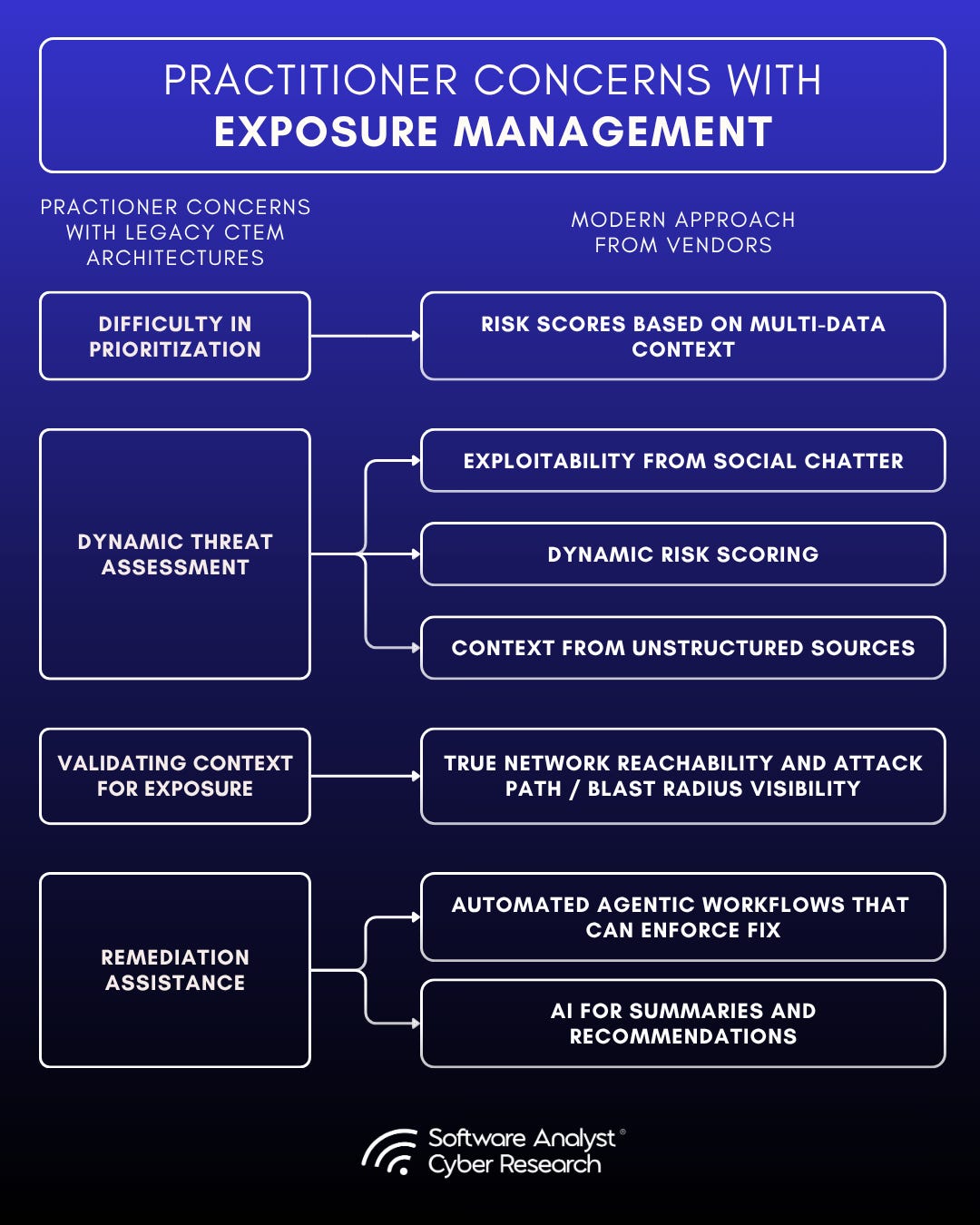
In 2025, the bottleneck isn’t whether you can scan everything. Most orgs already run multiple scanners. The result is fragmented visibility and higher operational overhead. The real challenge is unifying visibility and prioritizing true risk across fragmented environments. In short, risk priority is now a popular pain point over raw coverage.
Leaders emphasized the need for comprehensive visibility with contextualized risk priorities across all assets in increasingly dynamic environments. Practitioners consistently voiced the need for a single, unified coverage model that can give them visibility with an easy onboarding experience.
How vendors are addressing this -
Unified Visibility: Providing comprehensive coverage across all asset types including containers, code repositories, virtual machines, and cloud workloads in dynamic environments.
Broad Data Ingestion: Aggregating insights from multiple feeds such as threat intelligence feeds, exploitability databases, and third-party scanners for a consolidated risk view.
Beyond CVEs: Expanding scope to include insights on asset posture, coverage gaps, cloud security posture, identity exposure, data, business context and network context to create a complete picture of organizational risk.
Dynamic Threat Assessment
Crowdstrike’s global threat report 2025 reports the fastest eCrime breakout at 51 seconds, with average lateral movement occurring in under an hour. 79% of detections were malware-free, emphasizing identity and living-off-the-land tradecraft. Mandiant’s M-Trends 2025 reported that global median dwell time increased to 11 days, reversing years of decline. Meanwhile, Verizon’s 2025 Data Breach Investigations Report highlighted that vulnerability exploitation accounted for approximately 20% of breaches. Mandiant’s M-Trends 2025 report shows global median dwell time rose to 11 days. Add to this the rise in third-party and supply-chain exposure, plus the scale of GenAI-driven attacks, and the picture is clear: exposures have never been faster to exploit or broader in impact.
Defenders need platforms that can keep pace. That means staying current with the latest threats and delivering immediate context when a new vulnerability emerges. Security leaders want fast, clear answers to the question: “Am I impacted by this zero-day, and how high are the chances of its exploit in my environment?” Addressing that requires tools that combine discovery with business context and exposure validation so teams can focus on what matters most - fixing.
As one security leader said, “Don’t just show me what’s wrong, show me what I need to prioritize right now with the limited resources I have and show my team how to fix it”.
How vendors are addressing this -
Context-driven exploitability analysis: Increasing validation of exploitability based on attack paths, blast radius and other impact driven factors.
AI-assisted or agentic remediation workflows: Findings are automatically converted into tickets with full context and step-by-step guidance, routed to the correct asset owners via bi-directional integrations with ServiceNow or Jira to maintain true risk states.
Context for Exposure
If all we ever looked at was the severity rating that comes bundled with a vulnerability feed, every organization would end up with the same flat priority list. But reality does not work that way. Risk is not one size fits all; it is shaped by whether an asset is exposed to the internet, whether it is reachable, and how that environment is actually configured.
That is why a blanket score does not cut it. Two companies could have the same critical vulnerability, but for one it is buried behind layered defenses, while for the other it is sitting on a wide open asset in production. The stakes and the urgency are entirely different.
Security leaders do not just want to know what is theoretically severe; they want to know what is practically severe for their environment. Context, exposure, reachability, and attack surface are the layers that make vulnerability prioritization meaningful. Without them, security teams struggle to understand what truly demands urgent action in their environment.
Security leaders want dashboards that reflect context. Board metrics must show risk reduction, not just CVE counts. The priority is reducing exposure and protecting critical assets by ranking issues with reachability, exploit intel, control posture, coverage gaps and business impact.
How vendors are addressing this -
Reachability Context: Evaluating internet-facing assets, their network reachability, lateral movement paths, and overall attack path / blast radius.
Business Criticality: Prioritizing based on data sensitivity (PII) and business context such as production environment impact.
Compensating Controls: Factoring in network segmentation, EDR coverage, WAF protections, or IAM policy conditions to refine true exposure.
Exploit Intelligence: Integrating live threat data from CISA KEV, EPSS, and exploit feeds to identify active exploitation and probable attack vectors.
Layered Prioritization: Combining reachability, exploit intelligence, and attack path context to establish a more accurate, risk-based remediation order.
Remediation Assistance
In our interviews, leaders consistently said discovery is easy; fixing is the bottleneck. Platforms that help prioritize what to remediate next and integrate directly into workflows (e.g., ServiceNow, Jira) are seen as genuinely helpful. Dedicated FTEs (Full Time Employees) for operating security platforms is a norm that is breaking in the world of AI capabilities reducing the operational overhead. Practitioners want platforms that can enhance the operator’s experience and reduce the overhead on their teams.
How vendors are addressing this -
“Ops-Ready” Recommendations: Clear, technically precise steps written for operations teams, bridging communication gaps between security and development teams.
Smart workflow automation: Auto-assign tickets, bi-directional integrations with ticketing platforms to assess true risk state and track progress, was valued higher than just visualization.
Practitioner’s Guide to the Right Solution
Step by Step Framework to Identify which solution fits best for your organization’s use cases
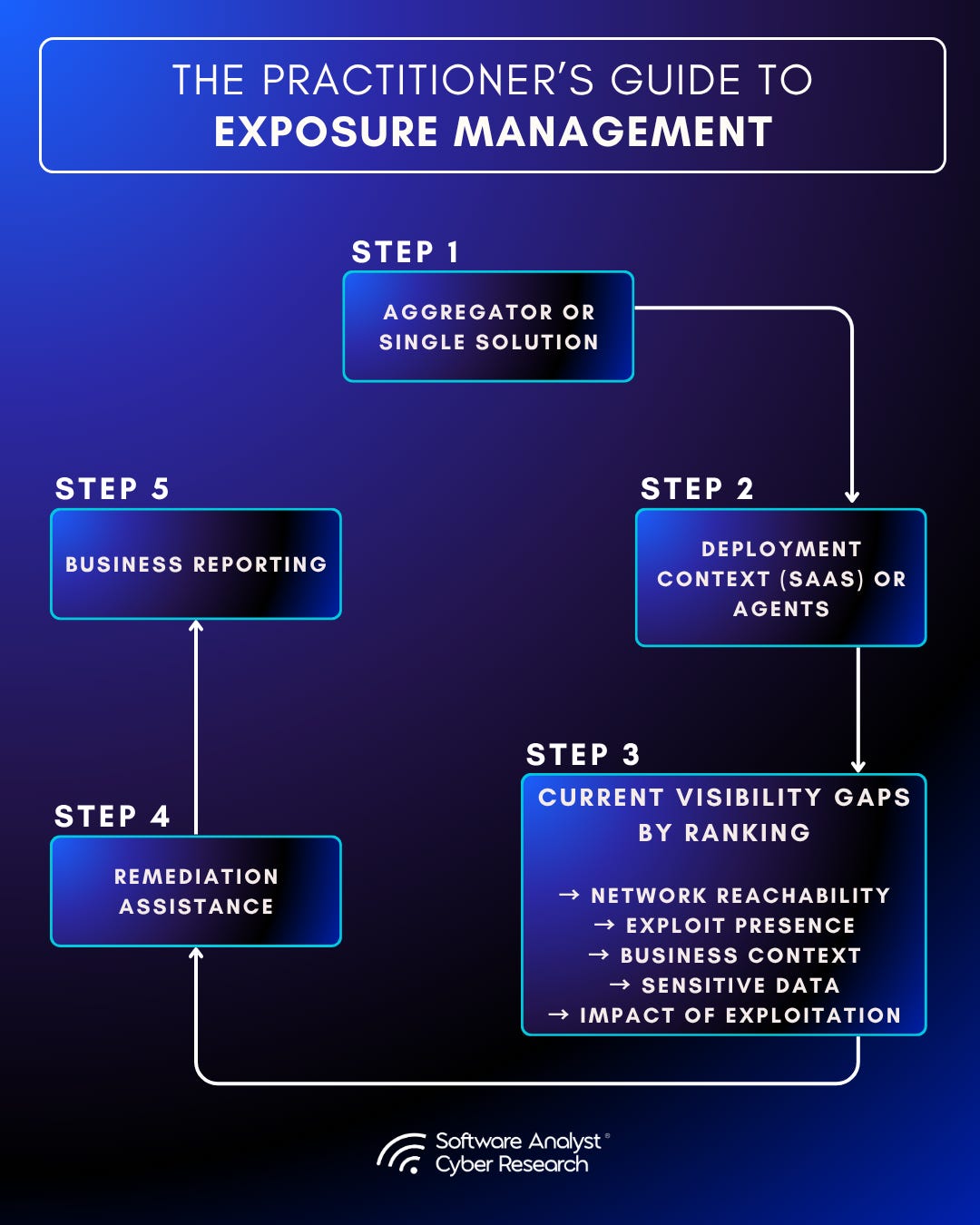
Step 1: Unification or Single Solution
The first step is determining whether your organization requires an aggregator or a single-platform coverage model.
Aggregator platforms consolidate findings from multiple scanners, cloud tools, and vulnerability systems into one unified remediation pipeline. These are ideal if you have a mature tool stack but struggle with normalization, deduplication, and operational orchestration.
Unified exposure platforms provide native scanning or posture assessment along with correlation and remediation workflows. These are typically preferred when consolidation and simplified deployment are higher priorities than maintaining multiple overlapping tools.
Step 2: Deployment Context
Check whether the solution fits the deployment model that is preferable in your organization.
Regulated or Sovereign Data Requirements: If operating in sectors such as finance, healthcare, or critical infrastructure, confirm that vendors can support on-premises or air-gapped deployment. Some modern platforms remain SaaS-only, which may not align with strict residency mandates.
Agentless vs. Agent-Based Collection: Evaluate whether you can deploy agents across workloads, endpoints, or cloud assets. Many platforms now use read-only APIs or network sensors to achieve visibility without agents.
Integration Overhead: Platforms with prebuilt connectors for scanners, ITSM, EDR, and cloud providers reduce time-to-value significantly.
Step 3: Map Current Visibility Gaps by Priority
Before evaluating features, document where your current exposure visibility is weakest.
Establish a top-down priority list across the following five visibility domains:
Area: Network Reachability Assessment
Guiding Question: Can you easily determine which vulnerabilities are externally reachable or exposed through internal routing?
(Look at vendors that excel in true network reachability via active simulation or other techniques)
Area: Exploit Presence
Guiding Question: Do you have real-time insights into exploitability factors?
(Look at vendors that go beyond EPSS and KEV feeds to determine probability of exploit)
Area: Business Context
Guiding Question: Can you easily connect technical assets to business criticality, owners, and sensitivity levels?
(Look at vendors that excel in deriving context, sometimes even looking at unstructured data sources or dev tools)
Area: Sensitive Data Visibility
Guiding Question: Are you able to easily identify assets with critical / sensitive data in it?
(Look at vendors that can provide in-depth data scanning (DSPM) capabilities beyond config reads)
Guiding Question: Impact of Exploitation
Can you easily visualize how one compromise could traverse identities, network, and data?
(Look at vendors with exploit paths and blast radius visibility)
Step 4: Evaluate Remediation Assistance
After prioritization, there is still the need for remediation which is your responsibility. It’s important to learn what assistance these platforms can provide in remediation operations.
Modern solutions now offer Remediation Operations (RemOps) or workflow automation that connect security and IT directly.
Automated Ticketing: Platforms generate and route contextualized remediation tickets directly into Jira or ServiceNow with ownership and SLA metadata.
Task Consolidation: Multiple CVEs or misconfigurations are merged into a single “fix item,” reducing duplicate effort.
Verification Loop: Closed tickets are automatically revalidated via telemetry syncs to ensure exposures are truly resolved.
Step 5: Business Reporting
This may not be an important factor for you if you create customized dashboards outside of the security tooling you use. However, if you do need this visibility from within the platform then you should consider these factors :
Custom Reporting and Dashboards: Look for platforms that allow dynamic filtering by context such as environment, business unit, or SLA.
Residual Risk Metrics: Ability to quantify how compensating controls reduce risk even before patch deployment.
Natural Language Summaries: Some platforms generate narrative summaries or executive-ready visuals automatically, aligning technical exposure with business impact.
Vendor Assessment Framework
Vision (Not a weighing factor)
What is the vision of the company for future readiness? What areas do they see their platform evolving?
Vendors
To understand key innovations pertaining to vulnerability risk and exposure management platforms in 2025, we did a deep dive into 10 vendors through in-depth product briefings, customer interviews and in-depth questionnaires, beyond marketing materials. We focused on core differentiators, and the approach they’re taking in addressing risk prioritization and exposure visibility concerns.
In alphabetical order and no particular ranking -
Astelia
Astelia is a cybersecurity firm currently in stealth, focused on exposure management through true network reachability analysis and preemptive exploitability assessment. The platform aims to help organizations defend against attacks by prioritizing reachable vulnerabilities before they are exploited in the wild.
Astelia’s solution leverages a customer’s existing security portfolio investment to gather findings while also querying networking devices like firewalls and load balancers to understand the path to a vulnerability. Their core focus is to provide exposure assessment based on network reachability analysis. The solution matches up the understanding of the runtime environment from the network’s perspective with the findings ingested to understand how ‘reachable’ the vulnerability is.
Once vulnerabilities are prioritized, bi-directional integrations with Jira and ServiceNow enable remediation and mitigation workflows, ensuring evidence-based prioritization drives faster mean time to remediation (MTTR).
Mapping Astelia’s capabilities against our analysis framework –
Deployment
The platform is a SaaS-only solution at this time, with the vendor stating that a self-hosted or air-gapped deployment is not currently available but is on the roadmap for the future. However, it does support hybrid customer environments for exposure analysis.
Data Collection and Correlation
Astelia provides Agentless deployment method and integrates with existing tools such as: vulnerability scanners (e.g., Qualys, Rapid7), EDRs (e.g., CrowdStrike, Defender), and network devices (firewalls, WAFs, load balancers, routers) via read‑only APIs. The data is pulled from other tooling and network devices on a configurable basis, with a default of once per day.
Data sources and collection:
Integrates with existing tools via read‑only APIs.: vulnerability scanners (e.g., Qualys, Rapid7), EDRs (e.g., CrowdStrike, Defender), and network devices (firewalls, WAFs, load balancers, routers)
Builds a topology graph that maps public to internal addressing, NAT, load balancers, and network paths to assets.
Frequency: default daily pulls, configurable by the customer.
Prioritization and Risk Factors
Astelia moves beyond CVSS scoring by taking into account -
Network Mapping: Analyzing network topology by integrating with network tools like firewalls, switches, and load balancers to map and model the environment.
Runtime context: Runtime context on the host, such as whether the vulnerable process/service is actually running
Exploit intelligence and threat context: Presence of known exploits, active exploitation, and whether a vuln is part of an “attack path” class that warrants urgent action
External severity feeds: CVSS, EPSS and KEV as inputs to determine severity scoring
Public Exploitability context: Astelia employs purpose-built AI agents to enrich vulnerability findings with contextual exploitation intelligence. These agents automatically gather and synthesize publicly available information (research posts, vendor advisories, exploit databases, and technical write-ups) and extract high-level signals about whether an exploit exists and what conditions it requires.
Attack path analysis: Provides a visualized attack path through network infrastructure to each reachable vulnerability.
Blast Radius: Blast radius and hybrid context, prioritizing items that materially increase lateral movement risk across on‑prem and cloud
Exploitability Assessment
Core differentiator: Network reachability analysis to filter the reachable and must-be-remediated vulnerabilities even without a public exploit.
Evidence‑based explainability: Provides proof of reachability and exploitability paths, and evidence from customers’ own tools for audit alignment.
When data is incomplete, Astelia biases toward reducing false negatives by assuming a vulnerability’s presence and then proving or disproving reachability with evidence from customer’s existing tools. This is the default setting, but configurable by the customer.
Remediation and True Risk State
Supplies remediation guidance to teams
Bi-directional integrations with Jira and ServiceNow support remediation and verification cycles.
Default bias toward detecting reachable exposures ensures low false-negative rates.
Astelia maintains the true risk state of an asset by providing bi-directional integrations with ticketing workflows.
Vision
Astelia’s vision is to evolve from vulnerability-centric Exposure Management (EM) toward a broader Enterprise Security Posture Management (ESPM) platform, extending beyond infrastructure to encompass identity, network hygiene, micro-segmentation, and deeper coverage across hybrid environments
Analyst Take
There are the strengths and areas to watch in our opinion
Strengths:
Risk-Based Prioritization: Goes beyond CVSS scores by factoring in reachability and network paths, helping security teams cut through noise and focus on vulnerabilities that are exploitable.
True Network Reachability and exploitation analysis: AI agents enrich vulnerability findings with exploit intelligence and conditions, while topology mapping and reachability analysis pinpoint only the vulnerabilities that are truly reachable and exploitable in the customer’s environment even if there is no public exploit record for the vulnerability.
Integration with Existing Security Investments: Leverages customer’s existing tools (vulnerability scanners, firewalls, load balancers, etc.), which reduces deployment friction and avoids requiring full-stack replacement.
Automation & Remediation Workflow: Direct integrations with Jira and ServiceNow as well as guidance on remediation plan, accelerate remediation by pushing prioritized findings into team workflows, reducing mean time to remediation (MTTR).
Hybrid Environment Coverage: Supports hybrid workload types (containers, hosts, on-prem + cloud).
Areas to Watch:
SaaS-Only Deployment: No on-prem/air-gapped deployment yet, which may block adoption by highly regulated sectors like government, critical infrastructure, defense.
Developer workflows: Roadmap items like integrations into developer workflows and tooling, more collaboration focused integrations will be valuable additions to their capability.
Axonius
Axonius has pivoted from pure cyber asset management to a broader exposure management platform built on its “Asset Cloud” and a large adapters catalog that aggregates and normalizes data.
The platform unifies asset aggregation and correlation across devices, software, identities, applications, and infrastructure, combining security scores with business context to help organizations prioritize and manage risk effectively. Key capabilities include AI-assisted recommendations, exposure management that integrates posture, exploit, identity, network, and application context, along with case management, workflows, and remediation recommendations.
Axonius has a broad definition on what it classifies as an asset - any entity with an identifier that can be part of a control plane. Domains served include asset management, devices, software assets, exposure, SaaS, and identities.
Voice of the Customer
We interviewed a customer of Axonius (Head of Information Security of a large and well known University). Here are opinions from customer on Axonius –
Life before Axonius
Before Axonius, the organization scanned known assets but lacked full visibility and had an overwhelming volume of vulnerabilities, making prioritization difficult and not fully knowing their asset coverage.
“The main challenge was we were getting too many vulnerabilities and so we had difficulty prioritizing them so that we could make sure that we’re focused on the most important vulnerabilities first.”
Why Axonius
The organization needed a reliable, comprehensive view of assets to ensure full coverage beyond just known assets. The customer mentioned that alternatives would have required separate vendors for CAASM/asset inventory and RBVM, whereas Axonius enabled them to consolidate both capabilities within a single platform.
“We worked with Axonius to enhance what we refer to as its Risk-Based Vulnerability Management (RBVM) capability… What we now focus on is probably five to 10% of what we told remediators to worry about in the past.”
What they would like to see more
Expanding into the CNAPP category, getting posture information, code repository and other tangential capabilities. They would like to use Axonius as their central visibility platform.
Mapping Axonius’ capabilities against our analysis framework
Deployment
The platform offers both SaaS and on-prem deployment options, providing flexibility based on customer requirements. It supports hybrid environments for comprehensive exposure analysis and is FedRAMP Moderate authorized, meeting the needs of government customers.
Data Collection and Correlation
Axonius provides an agentless deployment method and integrates with existing IT and security tools via read-only APIs. Many adapters are bi-directional with actions that support full CRUD operations. The platform aggregates and normalizes data from a wide range of enterprise systems beyond traditional vulnerability scanners.
Data sources and collection:
Integrates with Identity and access platforms (Eg: Microsoft Entra, Okta, Google), Code and developer systems (GitHub), EDR/XDR and endpoint management tools (Ex: CrowdStrike, Microsoft Defender), Vulnerability scanners (such as Qualys, Rapid7), CNAPP/CSPM and cloud providers(Wiz), SaaS and IT service tools, VM/asset inventories and CMDBs
Frequency: Data is collected on a configurable basis, with default daily synchronization from integrated systems.
Prioritization and Risk Factors
Axonius augments CVSS scores by taking the following factors into account
External severity feeds: CVSS, EPSS and KEV as inputs to determine severity scoring
Config Exposure: Determines internet exposure by reading into asset configurations from firewalls, load balancers, subnets, and cloud networking
Control gaps: Identifies control coverage gaps by correlating data across sources. For example detecting devices that lack expected EDR, and can trigger prebuilt queries and enforcement actions to close those gaps.
Business Context: Able to pull business context from asset labels to prioritize sensitive assets.
Asset Posture Context: Taking into account control gaps, internet exposure and configuration of asset
Exploitability Assessment
Core differentiator: Axonius ranks issues across devices, identities, SaaS, and cloud in one engine, so non-CVE exposures like missing SSO or mis-scoped identity permissions get scored alongside vulnerability severity for risk assessment.
Explainability: Exploitability and control-state validation via multi-source evidence
Using its Workflows engine, Axonius can automatically trigger a scan from an integrated BAS or pentesting tool (like Pentera) when a new high-risk exposure is found. It then ingests the results (e.g., “Exploit Verified”) back as another piece of context, which can be used to further escalate prioritization and mobilization.
Remediation and True Risk State
Bi-directional integrations with ticketing platforms via adapters to confirm state has actually changed, preventing stale or incorrect alerts from lingering
Risk scores are tied to ownership, SLAs, and bi-directional orchestration,
Along with integrations with ticketing platforms, Axonius provides case management within the platform as well to help users navigate remediation plans.
Axonius’s “Intelligent Action” includes:
Enforcement Actions: API-based actions to remediate issues, such as deploying an agent, isolating a device, creating a ticket, or deprovisioning a user.
Workflows: A no-code engine to build conditional logic for remediation (e.g., “If a device is missing an agent AND SCCM is available, deploy the agent; OTHERWISE, create a Jira ticket for the asset owner”).
Case Management & Ticket Binding: Creates cases within Axonius to track remediation progress and binds them to tickets in external systems (ServiceNow, Jira, PagerDuty), providing a closed-loop process to ensure issues are actually fixed.
Vision
Axonius aims to expand covered asset classes and domains (e.g., IoT/OT/CPS via medical‑device acquisition) while strengthening the risk and prioritization engine and full exposure lifecycle management .
Analyst Take
There are the strengths and areas to watch in our opinion
Strengths
Cross-domain visibility and correlation: Unifies devices, identities, SaaS, and cloud via adapters, normalizes and deduplicates into an asset graph.
Bi‑directional integrations: Trigger tickets or direct changes in IDPs, endpoints, SaaS, and cloud, then re‑verify via adapters. Ownership and SLAs support lifecycle management from finding to fix.
Asset Intelligence Context: Pulls from multiple systems via adapters, then normalizes and deduplicates to a single asset/entity before flagging an issue. Conflicts are reconciled at ingestion to avoid duplicate findings.
Control Gap: For each declared control, Axonius can identify exceptions such as devices missing CrowdStrike or users not under SSO.
Asset Ownership: Axonius provides metadata on asset ownership making remediation tracking easier.
Areas to Watch
Mature Recommendations: While the platform provides prescriptive reports, more opinionated recommendation steps can help users further reduce operational overhead
Integrations with existing platforms: The more data Axonius can pull, the better asset intelligence context it can provide. For organizations with distributed ownership, onboarding all integrations may take longer.
Cogent Security
Cogent takes an AI-native approach to exposure and risk management. The platform aggregates findings from scanners, cloud environments, identity systems, and infrastructure sources to provide consolidated visibility across assets, exposures, and ownership. It then uses AI agents and natural‑language tooling to help teams prioritize, assign, and drive remediation to closure.
Cogent does not perform scanning itself. Instead, it ingests and normalizes both structured telemetry and unstructured operational context such as data from tickets, documentation, and communication channels, building a continuously updated model of an organization’s security posture. The platform prioritizes remediation work based on exploitability, business impact, and exposure conditions, incorporating factors such as compensating controls, ownership, and change plans.
Cogent focuses on AI agentic integrations for reducing operational overhead by assisting in remediation workflows. Cogent deploys AI agents to open and route high-quality tickets, coordinate maintenance windows and approvals, manage SLAs and exceptions, bind ownership, and verify fixes. Humans stay in the loop for oversight and key decisions. Cogent’s goal is to reduce operational overhead and improve closure accuracy by automating coordination tasks while keeping humans in the loop for oversight and key decisions.
Voice of the Customer
We interviewed two Cogent customers, CISOs of well known enterprises. Here are their perspectives –
Life before Cogent
Leaders described a large backlog and fragmentation across environments. CNAPP covered production, but corporate and other footprints were unmanaged in one place. Prioritization was hard, reporting required hours of manual crunching, and execution struggled on ownership and workflow clarity.
“How we prioritize our body of work was really hard. Just like remedial things, like who owns system X and what is it used for? I mean, all these things were a challenge for us.”
Why Cogent
Customers cited quick time‑to‑value, an AI‑native experience that actually works alongside existing tools, and consolidation across production and corporate estates. They highlighted cost savings from reduced manual effort, stronger board‑level reporting, and prescriptive guidance that accelerates remediation.
Customer 1: “..That’s where really Cogent came into play. I’ve got enough tech that tells me what’s wrong. I don’t have enough tech that helps me fix it. We knew we wanted a kind of an AI native platform for this… We know what our exposures are. What we need help with is how do we manage this? Not like, do the work, but I mean like managing it like how do we prioritize risk?”
Customer 2: “Any kind of change that happens needs to be tracked and monitored. CNAPP tools are amazing. They provide you enormous visibility but they don’t take it to the next level. And I think it’s similar to the ASPM market. All those tools exist but you still need an aggregation layer. So that’s what Cogent did for us Cogent was basically an aggregator of all the vulnerabilities that you have in your corporate environment and in your production environment”
What they would like to see more
Deeper integrations for more context, continued expansion toward a unified pane across vulnerability types including AppSec, and steady strengthening of the data platform while keeping the “operator” experience.
Mapping Cogent’s capabilities against our analysis framework:
Deployment
Cogent Security is a SaaS based platform supporting customers’ hybrid environments.
Data Collection and Correlation
Cogent leverages an organization’s existing enterprise tool ecosystem, pulling the data agentlessly, for asset inventory, security context, and business intelligence to provide a unique persona driven view of prioritized actionable data with automation.
Data sources and collection:
Integrates with existing tools via read-only APIs: vulnerability and asset context content from CNAPP / CSPM, Identity and Access, EDR/endpoint, Network and Infrastructure, CMDB/ITSM, cloud audit trails, and source code platforms like Github
Prioritization and Risk Factors
Cogent moves beyond CVSS scores by taking into account the following factors -
External severity feeds: CVSS, EPSS, KEV, and live intel feeds to weight exploit likelihood
Internet Exposure: Cloud and network configs to assess reachability and blast radius
Control gaps: Missing or unenforced controls such as absent EDR agents or disabled SSO, detected via cross‑tool correlation
Business context and ownership: Criticality via asset labels and context from unstructured data, to bind ownership and work to SLAs
Asset Posture Context: Identity and permissions issues, mis‑scoped access, and other misconfigurations scored alongside CVEs
Dynamic state verification: Re‑syncs with integrated systems after actions are taken, to confirm fixes and prevent stale risk items
Public Exploitability context: The product supplements asset context with real-time threat intelligence from sources like GitHub, news articles, and social media to assess risk score
Unified risk scoring: Across CVEs and non‑CVE issues like missing EDR, mis‑scoped permissions, or control gaps
Prioritization is tailored to each organization, shaped by the business context and environment Cogent ingests, rather than relying on static out-of-box models that only let you adjust weightings.
Exploitability Assessment
Core differentiation: Ability to integrate unstructured data analysis, which allows Cogent to determine accurate ownership and prescriptive remediation plans. Another highlight is their exploitability research that factors in real-time signals from code repos, security disclosures, and social chatter to assess the likelihood of exploitation.
Explainability: Exploitability context informed by multi‑source threat evidence and live intel
Normalizes and deduplicates across devices, services, identities, and infrastructure footprints.
Closed‑loop verification via adapter re‑syncs after downstream changes occur, to prevent stale alerts; can orchestrate external validation workflows if available
Remediation and True Risk State
Cogent provides AI assistance across multiple aspects of reporting and remediation workflows.
Custom Reports: Cogent’s AI agent helps users process information through natural language queries, generate work audits, and produce comprehensive reports.
Managing Workflows: Cogent’s AI agent generates remediation tickets with context, justification, and step-by-step actions that can be audited before automation. The system adapts based on customer feedback and environment, preserving configurations for reuse and improving recommendation quality over time.
Enforcing Remediation: Cogent’s AI agent enforces remediation steps once approved by the user.
Vision
Currently, the platform focuses primarily on solving for overwhelmed vulnerability management teams, but looking to the future is evaluating integrations with SOC teams and providing native automation (vs. orchestration) through agentic platform expansion.
The company’s stated vision is to enable “decision offloading,” where the complex and time-consuming tasks of context-gathering, analysis, and decision-making are delegated to AI agents, freeing human experts to focus on strategic initiatives and complex exceptions.
Analyst Take
There are the strengths and areas to watch in our opinion
Strengths:
Cross domain visibility and context: Taking into account CVE and non-CVE factors like posture, identity, network exposure, exploit likelihood, SLAs and ownership into account while devising risk scores.
AI-Native NLQ and Custom Reports: Cogent can build custom comprehensive reports via AI capabilities to help with reporting to auditors and other stakeholders
Control gap: Cogent can check for missing controls in place such as missing EDR agent, to explain risk
AI assisted workflows: Reduces operational burden by recommending remediation plans and when allowed, enforcing upon them
Dynamic states: Resyncs after action is taken to ensure there are no stale risk states
Areas to Watch
AI remediation: There is currently no “undo” button for actions that the AI agent can take. Users have to manually track audit trails in order to revert.
SaaS only deployment: SaaS only deployment may make it difficult to expand into regulated industries.
Nagomi Security
Nagomi Security leverages an agentless approach to data intake from sources like device management, vulnerability scanners, identity management, threat intelligence, endpoint detection, and asset management (e.g. CMDB) solutions.
This data is then normalized and prioritized based on the asset, CVSS/EPSS score, threat intelligence of active campaigns, number of assets impacted, and any compensating security control gaps,e.g a ‘Toxic Exposure’.
Once the data is prioritized, remediation recommendations are shared via integrations with the ITSM modules of ServiceNow, Jira, Freshworks, and ManageEngine enables prioritized findings to reach the appropriate teams for remediation or mitigation.
Deployment and Data Ingestion
The platform is a SaaS-only solution at this time with support for hybrid customer environments for exposure analysis.
Nagomi Security provides Agentless deployment method and integrates with existing tools such as: vulnerability scanners (e.g., Qualys, Rapid7, and Tenable), EDRs (e.g., Tanium, Bitdefender), email security (e.g. Tessian and Defender for Office 365), and network devices (firewalls, WAFs, load balancers, routers) via read‑only APIs.
Risk Factors
Nagomi Security moves beyond CVSS scoring by taking into account -
Asset: Identifying business context of an asset mainly via tags pulled from CMDB integration
Exploit intelligence and threat context: Presence of known exploits, active exploitation and campaigns, including phishing
Identity: Identification of weak identification controls
External severity feeds: CVSS, EPSS and KEV as inputs to determine severity scoring
Compensating Controls In-Use: Identification of if a misconfiguration or prioritization is exploitable by also analyzing what compensating controls are in place and how they are configured.
Number of Assets Impacted: Since assets are the central entity construct, the number of assets affected by a misconfiguration or vulnerability is also a factor.
Core differentiator: Compensating controls viewpoint allows organizations to get more out of existing security tool portfolios.
Remediation
Nagomi Security provides step-by-step remediation and mitigation plans to work with ticketing workflows. However, currently the integration is one-way with validation of a remediation or mitigation occurring through continuous assessment.
Strengths:
Risk-Based Prioritization: Goes beyond CVSS scores by factoring compensating controls, misconfigurations, weak identities, and targeted threat campaigns to help prioritize what security and IT teams need to focus on.
Exploitability with Compensating Controls Nagomi Security’s AI capability looks at compensating controls beyond firewall configurations to get more out an organization’s security investment while reducing exposure.
Integration with Existing Security Investments: Leverages customer’s existing tools (vulnerability scanners, firewalls, load balancers, etc.), including security awareness and identity not only reduces friction with lift and shift replacement but also give a more holistic view to a security program effectiveness
Automation & Remediation Workflow: Direct integrations with Jira and ServiceNow and guidance on a remediation plan, accelerate remediation by pushing prioritized findings into team workflows, reducing mean time to remediation (MTTR).
Areas to Watch:
SaaS-Only Deployment: No on-prem/air-gapped deployment yet, which may block adoption by highly regulated sectors like government, critical infrastructure, defense.
Orca Security
Orca security, known for introducing and patenting SideScanning™ architecture, approaches vulnerability exposure management from a CNAPP foundation. As a CNAPP platform, Orca consolidates posture, vulnerability, data, network and identity risks into one platform to drive more effective exposure management and prioritization.
Orca’s approach centers on correlating misconfigurations, vulnerabilities, identities, network exposure, and data sensitivity into a connected “attack-path” security graph. The platform highlights risk in context, surfacing exposures that are both exploitable and impactful based on CVE and non-CVE factors. Its dynamic scoring model ingests from feeds such as EPSS and KEV with additional signals such as internet-facing status, sensitive data detection, and validated attack paths to reflect the true risk of a vulnerability.
Orca AI provides detailed remediation guidance across multiple methods, including Cloud Console, CLI commands, CSP deployment templates, Terraform, Pulumi, and OPA policies. Users can also apply fixes directly from the Orca console. The platform includes natural language search for querying cloud environments with plain language questions and an AI Assistant (in private beta) that helps investigate risks, interpret environment data, and support faster decision-making using insights already available within the platform.
Mapping Orca’s capabilities against our analysis framework
Deployment
Orca is primarily deployed as a SaaS platform but provides the option for the snapshot based scanning to happen in customer’s cloud accounts while only taking metadata into the Console (managed by the vendor). Orca also offers a private mode, where the backend and scanning runs entirely in customer accounts, and no data or metadata ever leaves it.
Data Collection and Correlation
Orca Security uses direct cloud provider APIs and snapshots to collect asset inventory, read configuration and patch data across virtual machines, containers, serverless, storage, IAM, and networking.
Data sources and collection:
Cloud providers - AWS, GCP, Azure,Oracle Cloud, Alibaba Cloud, Snowflake, Tencent Cloud, on-prem deployments, Code repository platforms like Github, ingests data on network context - loadbalancers, VPC flow logs, data storage platforms such as S3 buckets, identity information (IAM) and asset configuration
Orca Sensor (runtime protection in private beta) now supports other public cloud and private cloud environments, as well as on-premise environments. Covers AI and Machine Learning (ML) inventories with AI Security Posture Management (AI-SPM).
Prioritization and Risk Factors
Orca moves beyond CVSS scoring by taking into account -
Exploitability and exposure: Internet reachability, security group rules, route paths, and identity permissions to assess whether a vuln is actually reachable
Identity and privileges: Excess or mis-scoped permissions that turn defects into exploitable paths
Data sensitivity: Detection of sensitive data and potential blast radius if exploited
Cloud posture: Misconfigurations across storage, network, and workload baselines that amplify risk
Attack-path context: Correlates multiple weaknesses into toxic combinations that represent real-world breach paths
External Feeds: OS vendor specific feeds, EPSS, KEV
MITRE Framework: Comparison against MITRE attack techniques
Business and asset context: Derived from asset tagging and data sensitivity signals
Scores by reachable attack paths, sensitive-data impact, and identity exposure.
Exposure Assessment
Core differentiation: Orca’s CNAPP foundation allows adding in-depth context from cloud asset configurations and other CNAPP pillars (such as CIEM and DSPM) directly into risk scoring calculations.
Explainability: Prioritizes with agentless and dynamic reachability analysis, which identifies vulnerable packages that attackers can reach in production.
Builds an attack path security graph based on asset configuration, identity policies and posture to determine blast radius. Provides attack-path recalculation and state re-checks after changes to confirm risk reduction and prevent stale findings
Remediation and True Risk State
Bi-directional integrations with ticketing platforms (e.g., JIRA), SOAR, and SIEM systems enable seamless workflow connectivity.
Provides in-platform remediation guidance with the option to apply fixes directly, to reduce operational burden.
Supports dynamic intelligence sharing and automatic validation of issue resolution across connected systems.
Orca’s dynamic alerts automatically update in ticketing systems as statuses change and verify issues are resolved once tickets are closed, maintaining the true risk state of an asset.
Vision
Orca’s vision is to incorporate deeper AI features in remediation workflows, moving towards an automated remediation platform.
Analyst Take
There are the strengths and areas to watch in our opinion
Strengths
CNAPP Foundation: In depth capabilities related to workload, posture, identity and network pillars - all combined into risk scoring and exposure calculations.
Attack Path Analysis: Attack-path “security graph” that correlates identity, network, and data context to surface toxic combinations.
AI assisted Remediation: Detailed remediation plan to help users identify what steps to take.
Cloud to code tracing and remediation: Production risks are traced back to their source code, with the option to remediate the source issue from production.
In-house scanning: Orca provides its own scanning instead of depending on other vulnerability scanners. Customers can start using Orca without needing other security stack to be in place.
SCA and open-source posture: Software composition and license signals roll into the same prioritization logic, so packages and third-party components influence exposure decisions alongside infrastructure and identity signals
Areas to Watch
Limited Aggregation Flexibility: Orca is a pure-play CNAPP solution and does not aggregate vulnerability data from other scanners or existing security tools. Organizations seeking a unified exposure view across multiple scanners or hybrid ecosystems may find this restrictive.
AI Assistant Early Stage: The AI Assistant is currently in private beta, with limited visibility into its decision accuracy, contextual understanding, and enterprise-readiness.
Seemplicity
Seemplicity approaches vulnerability exposure management from a vendor-agnostic orchestration foundation and remediation operations (RemOps) focus. Rather than conducting its own scans, Seemplicity consolidates findings across vulnerability, AppSec, cloud, and infrastructure scanners into one unified remediation pipeline, normalizing and deduplicating issues and prioritizing them according to business context. A key focus is aggregating items with a common fix, with a goal to reduce the number of findings and accelerate overall risk reduction.
Seemplicity emphasizes consistent cross-domain prioritization through customizable rules, scopes (collections of assets), and filters (finding attributes). Customers define their own severity tiers (P0, P1, P2, etc.) and can query findings with a combination of these tiers with other environmental factors, creating a shared language across exposure domains. The result is a centralized exposure management platform with exposure factors ingested from the existing security stack.
Seemplicity can create customized or templated workflows via its Exposure Action platform with integrations to issue tracking systems like Jira and ServiceNow. These integrations are bi-directional to reflect the true risk state of an asset.
Mapping Seemplicity’s capabilities against our analysis framework
Deployment
Seemplicity is deployed as a SaaS platform. It also supports deploying on-premise agents for connecting to on-premise data sources or ticketing systems.
Data Collection and Correlation
Seemplicity ingests data from customer’s existing security stack via API integrations with data sources such as vulnerability scanners, code repositories, ITSM, SIEM, and other operational systems. Instead of scanning, the platform consolidates, deduplicates, and normalizes imported findings to serve as the central exposure management and remediation orchestration layer.
Data sources and collection:
Vulnerability scanners such as Qualys, Tenable, Rapid7, AWS Inspector, Fortra VM, Wiz, SAST / DAST tools like Checkmarx, GitHub Advanced Security, Code Repositories such as Github, External attack surface management (EASM) and internet exposure tools, ASPM platforms such as Ox Security, Ticketing, workflow, and notification systems such as Jira, ServiceNow, or Slack
Prioritization and Risk Factors
It’s important to note that Seemplicity’s finding severity is user-defined through a 1:1 mapping that incorporates threat‑signal enrichments like EPSS likelihood and KEV status during prioritization. Users can then query findings using different combinations of factors that incorporate this severity along with other contextual information.
External Feeds: CVSS, EPSS and KEV as inputs to determine severity scoring
Business Context: Business criticality of the asset based on asset label or ownership information
Config Exposure: Determines internet exposure by analyzing asset configurations from firewalls, load balancers, subnets, and cloud networking
Runtime Context: Takes into account whether a vulnerable component is actually present/loaded and reachable
Control Gaps: Validate defenses-in-place
Seemplicity enforces a consistent, user-defined priority model across all asset types - VM, AppSec, cloud, and EASM. Priorities are user defined. The rule creation process includes “Scope”, which captures where the issue resides (collections of assets, applications, or environments), and “filters”, which captures attributes of the finding itself - like EPSS score. These rules translate severity with user defined context into standardized priorities (P0, P1, P2, etc.).
Seemplicity encourages a simple 1:1 mapping between context and priority levels, avoiding (but supporting) complex combinations in the priority definition process. Once priorities are mapped, users can query findings by combining priority levels with additional context signals such as runtime and reachability, business criticality, internet exposure, and exploitability.
Exploitability Assessment
Core differentiator: Uses an evidence-based exploitability model that correlates CVE, configuration, and runtime data from existing tools to determine real exposure, validating exploitability through multi-source context rather than relying solely on static threat feeds.
Explainability: The platform supports validation through multiple data sources, allowing teams to trace why a vulnerability is considered exploitable based on actual exposure evidence.
In case of conflicting feed severities, Simplicity defaults to the highest score but allows customers to configure preferences for specific scanner scores priority.
Remediation and True Risk State
Seemplicity’s Exposure Action Platform assists teams by reducing operational overhead with automated workflows enriched with risk priority and asset ownership context -
RemOps and Workflow Automation
Reduces operational overhead by automating workflows with embedded risk priority and asset ownership context. Seemplicity also leverages AI Agents to enhance automation through guided remediation, contextual insights, and intelligent task routing.
Case Management
Automates routing into tools like Jira or ServiceNow, enabling fixing teams to accept, clarify, or reject tasks while remaining accountable to SLAs. Bi-directional integration ensures ticket status and asset context are updated to reflect the true risk state after action.
Reporting and Visibility
Provides dashboards and metrics to track SLA compliance, remediation progress, and overall risk reduction, giving both technical and leadership teams clear visibility. The AI Insights capability can transform dashboards into actionable intelligence, surfacing key trends, blind spots, and posture changes automatically.
Vision
Seemplicity states that they are investing in AI assisted features to further deepen their remediation operations capabilities, with a continued focus on time to value and ease of use. The goal is to become a full AI-driven Exposure Action Platform that operationalizes risk reduction by aggregating findings from disparate tools, prioritizing them intelligently, and driving faster remediation with minimal complexity.
As the platform develops, Seemplicity aims to expand its guidance and automation features to support exposure management for organizations of varying sizes and security maturity levels.
Analyst Take
There are the strengths and areas to watch in our opinion
Strengths
Remediation workflows - Helps users automate, route, and sync remediation work with ticketing platforms, including bidirectional updates and consolidation of multiple findings. AI Agents accelerate remediation by automating guidance, ownership, and insight generation across the workflow.
Broad integration ecosystem: Native connectors for VM, SAST/SCA/DAST, CNAPP, EASM, threat feeds like EPSS and CISA KEV, asset inventories, and ITSM, enabling rich context.
Priority model and rules engine: Uses consistent priority language across domains with customer-defined rules built from “scope” and “filters,” aligning remediation language organization-wide
Context beyond CVSS: Incorporates exploit likelihood (EPSS), KEV, business criticality, internet exposure, and where available, runtime/reachability signals from connected sources
Aggregator: Deduplicates, aggregates by the fix, and normalizes findings, creating a central repository for exposure data.
Areas to Watch
No in-house scanning: Does not provide in-house scanning, hence not suitable for organizations that don’t already have a security stack in place.
Separation between priority mapping and contextual searches: Priority levels are defined through rule mapping, while broader analysis such as combining priority levels with additional context signals is performed through searches. This two-step process can add complexity for some users.
Tonic Security
Tonic Security is a cybersecurity startup that recently emerged from stealth. Tonic focuses on reducing exposure by combining asset discovery, organizational context, threat intelligence, business impact assessment, and adversarial validation to prioritize remediation efforts.
Tonic’s approach to exposure management centers on an AI Data Fabric and a security knowledge graph that ingest structured and unstructured data, add business context, and cut false positives so teams can focus on issues that materially impact the organization.
Key capabilities include large‑scale data collection and harmonization, contextualization of findings with business impact, business process graphs and agentic workflows that accelerate mobilization from finding to fix. The platform aims to reduce tool pivots, provide a business‑led view of posture, and slash remediation time across vulnerability and exposure workflows.
Mapping Tonic Security’s capabilities against our analysis framework
Voice of the Customer
A customer of Tonic sent us their reasoning for choosing Tonic security for their exposure management program. His opinions below -
Life before Tonic
Before adopting Tonic, customer’s risk and exposure management program faced several key limitations and critical gaps:
Lack of Business Contextual Intelligence, siloed data: Critical business and operational data were scattered across systems like Jira, Confluence, Office365 emails/Teams, and GLPI, limiting visibility and slowing down decision-making. Manual Processes, Limited Business Alignment: Security tools lacked the ability to map technical findings to business impact, making it hard to prioritize based on risk to key processes. Compliance Blind Spots and Fragmented Data Sources
“Asset intelligence was slow and fragmented. Enriching assets with actionable context took hours or days and happened frequently, making triage and prioritization inefficient.. Much of the vulnerability management relied on manual collection and correlation, which increased response times and reduced agility… Security tools lacked the ability to map technical findings to business impact, making it hard to prioritize based on risk to key processes. Risk data was scattered across multiple systems, making it difficult to get a unified view of exposure.”
Why Tonic
“AI-Powered Business Contextualization: Its data fabric automatically analytics extracts and harmonizes context across business, organizational, and operational dimensions, enabling faster and more accurate triage
Efficiency and Focus: Our team moved into “beast mode,” achieving more with existing tools, reducing false positives, and gaining control over information silos
Automated Insights: AI-driven analytics that surface hidden risks and provide actionable recommendations without manual intervention.
Unified Risk Intelligence: A centralized platform that aggregates and normalizes data across silos, giving us a real-time, holistic view of risk exposure.
Trustworthy Reasoning: Tonic’s transparent and explainable logic gave you confidence in its outputs, allowing for decisive action without second-guessing
Accelerated Remediation: Mean Time to Respond (MTTR) dropped significantly, and ownership of assets became clearer, improving accountability and reducing exposure windows”
What they would like to see more
“Deeper Integration with On-Prem Systems: Expand and streamline integration with Jira, Confluence, and other legacy systems to ensure full context extraction across hybrid environments. In addition, adding seamless ingestion of vendor and supply chain risk data to expand exposure visibility beyond internal systems
Enhanced Visualization of Business Blast Radius: Improve the UI/UX for mapping asset impact on business processes - make it more intuitive and actionable for both technical and non-technical stakeholders with customizable dashboards and Predictive Risk Alerts
Continuous Feedback Loop for Context Accuracy: Introduce mechanisms for users to validate and refine the context Tonic generates, ensuring it evolves with organizational changes and remains aligned with business priorities”
Deployment
Tonic supports flexible deployment options, including SaaS, on-premises, and fully self-hosted air-gapped deployments, particularly suited for regulated sectors such as financial services. Their default preference is SaaS deployment.
Data Collection and Correlation
Tonic aggregates and deduplicates data from a wide range of sources, including ITSM systems, CMDBs, EDR/XDR tools, IDPs, virtualization, and backup platforms. Beyond standard integrations with existing vulnerability scanners, Tonic also natively scans, ingests, indexes, and analyzes unstructured data sources, such as institutional wikis, collaboration tools, and messaging systems, to discover assets and extract business/organizational context (e.g., asset criticality). This enables discovery of assets beyond regular methods, with automatic contextualization.
Data sources and collection:
Vulnerability scanners (e.g., Tenable, Qualys, Rapid7), ITSM and ticketing systems (e.g., ServiceNow, Jira), EDR/XDR tools (e.g., CrowdStrike, SentinelOne), Identity providers and CMDB platforms, Collaboration and knowledge management systems (e.g., Confluence, Slack, Microsoft Teams, Google Workspace), Virtualization and backup solutions.
Prioritization and Risk Factors
Tonic Security moves beyond CVSS scoring by taking into account -
Business Context: Unlike traditional methods of deriving business context, such as from asset labels and asset config, Tonic derives context automatically from unstructured data sources and messaging platforms by considering additional factors like:
Asset criticality.
Business processes enabled by assets (hosts, applications).
Number of high privileged users logged in.
Sensitive data that may reside on the asset.
Ownership Context: Ownership at the individual, team and departmental levels, structural dependencies, and hierarchy alignment.
Operational Context: Asset function, patch status, system dependencies, and business process posture maturity (a unique differentiator).
Temporal Context: Recency of detection, exploitation timelines, change frequency, patch cadence, as well as asset lifecycle and history.
Network Reachability: Reachability of assets (e.g., internet exposure derived from asset and network config.)
External Feeds: Exploitability of findings (e.g., KEV, EPSS and other databases), threat intelligence insights, and resilience of assets/control gaps (e.g., lacking recent backup or missing EDR agents).
Tonic consolidates all ingested data into contextualized views: business, organizational, geographical, operational, temporal, and adversarial, forming its “Six Degrees of Context” framework. A key differentiator is its ability to automatically extract business, operational, and organizational context from unstructured sources such as ITSM tickets, Notion, Slack, Confluence, and email, without needing manual input. This allows automated inference of asset criticality, role, and interdependencies across the application ecosystem, enabling dynamic and accurate prioritization.
Exploitability Assessment
Core Differentiator: Tonic integrates with ITSM, EDR and other security systems for asset discovery, and extends visibility into institutional knowledge bases and collaboration tools to uncover shadow assets and exposures. Its integrations with internal knowledge bases and collaboration tools help surface assets and dependencies that exist outside conventional inventories. For example, Tonic can identify assets referenced in IT tickets or business continuity plans that are missed by conventional scanners.
Another differentiator is Tonic’s business dashboard which provides a high-level, process-centric view of risk, helping CISOs and GRC teams understand how business operations map to security exposure.
Explainability: The platform includes a confidence algorithm that validates the reliability of attributed context within its knowledge graph. It evaluates data volume, recency, source credibility, coherence, coverage, and user feedback to generate a transparency score. This provides visibility into how trustworthy contextual information is. It also validates the reachability of assets and simulates potential business impact through blast radius visualization.
Tonic allows organizations to define data source precedence (for example, ServiceNow as the system of record) to reconcile conflicting data inputs. A human feedback loop enhances recommendation mechanism, allowing users to validate or challenge attributions, enabling the model to improve reliability and accuracy over time.
Remediation and True Risk State
Enables end-to-end remediation workflows by identifying responsible owners, initiating tickets, tracking fixes, and managing exceptions through compensating controls or risk acceptance processes.
Uses agentic automation to help security teams understand remediation progress and the impact of changes.
Integrates with ticketing and workflow systems such as Jira and ServiceNow to support automatic task assignment, ticket creation, exception handling, and remediation tracking.
Employs domain-specific agentic AI to enrich downstream systems like CMDBs and SIEMs, keeping contextual data consistent as exposures evolve.
Maintains an accurate view of asset risk by verifying remediation outcomes through integrations with scanning and patching tools, and identifying root causes when discrepancies occur.
Vision
Tonic’s vision centers on making context the core principle of exposure management. By helping security teams determine what truly matters and why, and by mapping risk to business processes, the platform aims to reduce data noise, improve cross-functional communication, and streamline decision-making.
Analyst Take
There are the strengths and areas to watch in our opinion
Strengths
Automatic business context from unstructured data: Tonic extracts and normalizes context from tickets, wikis, Slack/Teams, email, and docs to auto-populate business, operational, and organizational context for each asset, uncover shadow assets, and classify crown jewels without manual input.
Confidence scoring with transparent evidence and human feedback: A confidence algorithm scores each attribution using data volume, recency, source quality, coherence, and coverage, while users can upvote or downvote and suggest corrections to continuously improve accuracy.
Flexible Deployment Options: SaaS, on-prem, and airgapped
Process Graphs: Mapping exposure to process graphs
Automation & Remediation Workflow: Domain specific agentic AI provides strong automation capability to drive down MTTR but also keep other relevant systems and teams up to date as exposure changes.
Areas to Watch
Lack of Validation Phase Capability: Full attack path analysis is described as upcoming, so current depth of validation may be insufficient for teams seeking proof of exploit paths.
Reliance on installed tools and data within: Value is driven by ingesting many third-party sources and unstructured content. Gaps, conflicting feeds, or weak data hygiene can reduce accuracy.
XM Cyber
XM Cyber approaches exposure management through continuous attack path modeling. An exposure is treated as a sequence of exploitable weaknesses that can lead from an initial breach point to a critical asset. The platform ingests exposures beyond CVEs, including misconfigurations, permissions, overprivilege, and behavioral anomalies, then prioritizes by business impact through attack path analysis and choke point reduction (intersection of several attack paths).
The platform runs passive network scans, performs external attack surface scans, deploys lightweight sensors on workstations, servers, and domain controllers for Active Directory, and connects to cloud environments by API. It also pulls configuration from some security tools to understand deployed controls. This evidence feeds a digital twin knowledge graph used for validation, prioritization, and reporting.
Results from the attack path scenarios are then aggregated into ‘choke points’ which summarize which entities are part of the most attack vectors to critical assets to help teams prioritize where to start their remediation or mitigation efforts.
Remediation guidance can then be sent to applicable teams via ticketing integrations. XM Cyber can also enrich SecOps teams’ alerts and events with asset reachability, choke points, MITRE ATT&CK techniques, and exposure events to help with understanding what additional assets might be at risk through interconnectivity and lateral movements.
Voice of the Customer
We interviewed a customer of XM Cyber, a Group CISO at a large insurance and reinsurance firm. We also received questionnaire responses from another customer that are included in quotes. Here are opinions from the customer on XM Cyber -
Life before XM Cyber
The team struggled to understand true risk across complex data center environments and where to focus limited IT effort. Traditional scanners were in place but produced high volumes and did not tie issues to attack paths.
“And if I can understand my risk, I can put better defenses in place. And also, it’s where I can focus my efforts… If I can reduce time spent to fix what matters, there is clear ROI”
Customer 2: “We had a long-term problem in that we found it easy to identify new and existing vulnerabilities across our large and complex IT estate, but found it hard to progress remediation of those vulnerabilities in many cases, due to dependencies between vulnerable software components and critical application software that we could not disrupt.”
Why XM Cyber
XM Cyber was selected to continuously model breach entry points and attack paths, prioritize chokepoints, and blend vulnerabilities with misconfigurations for a truer picture of exposure. The customer highlighted strong, plain-language remediation with multiple actionable options that IT can execute without security translation.
“And the reason why I said the quality of the reader mediation advice, when I go to other security tooling vendors, they will say, apply this fix, okay? Sometimes it’s a bit more difficult than that, and same if you’re doing a configuration. If I go to XM Cyber, oh wow, it’s given me three choices, and it’s in a language. I do not need a security person to interpret that to an IT person. “
Customer 2: “The value that XMCyber has brought to us is a more targeted and more rapid reduction in the overall volume of vulnerabilities, with a magnified result in terms of reduction in actual cyber risk, proven by the results of the Attack Path Mapping that the tool enables. This has meant that we can take the vulnerabilities not prioritised and look for remediation opportunities more aligned with the regular cadence of application development and infrastructure maintenance, thereby spreading the work involved over a more manageable timeframe and workload.”
What they would like to see more
The customer noted that they would like to see XM Cyber wrap their capabilities in MCP. Provide MCP style chat interface and agentic AI that would allow junior analysts to ask natural-language questions and automate actions.
“I think of an LLM chat interface. I can write in plain English. A junior analyst can write in plain English several questions surrounding XM Cyber’s capabilities in context... Give us MCP tools, wrap your capability in MCP.”
Customer 2: “There are many opportunities for XMCyber to expand the functionality of the core tool to encompass more of the upstream vulnerability discovery and downstream remediation functionality, especially as regards configuration vulnerabilities. This will add further value through tight integration and reduction in tool diversity.”
Mapping XM Cyber’s capabilities against our analysis framework
Deployment
The platform is available as a SaaS solution and can run on AWS, GCP, and STACKIT (the European sovereign cloud from Schwarz Digits).
Customers can also run the platform on-premises, or in their STACKIT private cloud deployment.
Data Collection and Correlation
XM Cyber gathers data around exposures through either its own agents or by connecting to a resource via API.
Data sources and collection:
Integration with cloud environments to ingest configuration details, lightweight sensors on domain controllers, and optionally on servers and workstations, for Active Directory and endpoint context, Cloud provider APIs for assets, configurations, and identities across major clouds, including Stackit, Security control configurations pulled from existing tools to understand compensating controls and posture, Third party inventories such as CMDB for labels, ownership, and metadata, Web application scanners for application asset labeling and findings ingestion
Prioritization and Risk Factors
XM Cyber moves beyond CVSS scoring by taking into account -
Attack path analysis: Takes into account factors such as misconfigurations, permissions, each attack technique mapped to MITRE ATT&CK framework and also including hop count and exploit conditions on each node
Process view: Map breach points to critical assets and potential impact to business processes.
Choke point analysis: Identify intersections that collapse multiple attack paths with one fix
Internet Facing: External exposure linkage when an attack path connects to internet-facing assets
Complexity: Average of how many steps to compromise an asset from a breach point
Business Criticality: Identification of business assets at risk via tags &/or labels
Number of Assets Impacted: The number of assets impacted by a scenario or campaign
Coverage Gap: Identifying the absence of deployed EDR agents
Scoring combines threat intelligence data such as severity and real-world exploitability with XM Cyber’s attack graph analysis, which factors in exploit complexity within the customer’s environment and potential impact on critical assets. The goal is to provide a combination of complexity, business impact, and a “chokepoint ROI” score that estimates the level of risk reduction achieved per unit of remediation effort.
Exploitability Assessment
Core differentiator: XM Cyber’s core differentiator is their Choke Point ROI model, which identifies intersection points where multiple attack paths converge and prioritizes those fixes that deliver the greatest overall reduction in business risk.
Evidence-based explainability: Each attack technique carries conditions for exploitation. The platform checks system state and compensating controls on affected assets to decide whether the exposure is actually exploitable. Internal validation uses graph conditions and control state. External validation uses active tests to confirm exposure where appropriate.
Remediation and True Risk State
Integrates natively with ticket management platforms like Jira, ServiceNow, email and messaging.
Supports integration with SIEM and SOAR solutions and bi-directional SecOps tooling as part of a shift anywhere approach.
Provides multiple remediation options and alternatives when patching is not possible, with step-by-step guidance
Integrations with ITSM and messaging tools to route and track work, and continuous verification to close the loop on fixes and update security scores
Analyst Take
There are the strengths and areas to watch in our opinion
Strengths
Risk-Based Prioritization: Redefines how organizations approach risk and prioritization by focusing on attack paths and internal exploitability validation through system conditions and control posture, complemented by external autonomous testing for internet exposure.
Chokepoint ROI: Intersection of attack paths analysis to maximize risk reduction with minimal changes
Integration with SecOps: The bi-directional integration with SecOps platforms like Google’s SIEM allows both exposure management and SecOps teams to be more effective in understanding what types of attacks are being seen as reducing an attack’s impact by understanding exposure.
Automation & Remediation Workflow: Guidance on remediation plan, and providing multiple options to risk reduction when patching isn’t feasible.
Hybrid Environment Coverage: Supports hybrid workload types (containers, hosts, on-prem + cloud).
Areas to Watch:
Developer Focus: Roadmap items like integrations into developer workflows and tooling, more collaboration focused integrations will be valuable additions to their capability.
Integrations with external feeds: Currently a roadmap item, but the platform can benefit from integrations with external threat intelligence platforms.
Zafran
Zafran approaches vulnerability exposure and risk assessment from a unified asset inventory lens, enriched with runtime, reachability, and threat intelligence as the foundation for effective exposure management. Its core focus is contextual analysis of vulnerabilities, factoring in runtime presence, internet exposure, compensating controls, and threat actor activity, then translating these into AI-optimized remediation workflows via RemOps.
Zafran’s model aggregates, normalizes, and de-duplicates vulnerability signals across hybrid cloud and on-prem environments into a single source of truth.. With Zafran Discover, customers have the ability to do native vuln detection without deploying new agents.
The introduction of the RemOps engine underscores Zafran’s focus on bridging Security and IT: automating remediation by consolidating overlapping CVEs into aggregated tickets, auto-routing tasks in Jira/ServiceNow, and aim at reducing MTTR. It streamlines planning by consolidating vulnerability findings into actionable work items, grouped by affected components and assets, while tagging asset owners for clear visibility. The module provides both remediation and mitigation options, quantifies risk reduction from mitigations, and highlights where existing defenses have already lowered risk.
Their focus is to enable executive risk reporting that quantifies residual risk, demonstrates ROI of security controls already in place, and provides continuous visibility to leadership. Ongoing investments in agentic remediation are designed to further automation and reduce the operational burden on vulnerability management teams.
Voice of the Customer
We interviewed a customer of Zafran (a CISO of a large and well known enterprise). Here are opinions from customer on Zafran –
Life before Zafran
Before Zafran, their Vulnerability Management program identified many vulns but struggled to prioritize by actual risk; teams were overwhelmed by volume.
“We were throwing tons of vulnerabilities at the dev teams and the infrastructure teams. So for us going to Zafran was really to take a better risk‑based approach to identifying what they really need to focus on first and set our SLAs.”
Why Zafran
Zafran let them integrate with their existing security stack seamlessly showing ROI within a short time of onboarding and help reduce the manual effort required to maintain an active risk assessment.
“Zafran allowed us to integrate existing security tools to assess how protections in place could reduce vulnerability risk.”
What they would like to see more
More integrations with AppSec tools, security configuration management, and custom integrations.
Mapping Zafran’s capabilities against our analysis framework
Deployment
The platform is SaaS-only, though it supports hybrid customer environments for analysis.
Data Collection and Correlation
Zafran employs an agentless approach to gather and normalize data from scanners, cloud security tools, and other components of a customer’s security stack. Beyond scanner ingestion, Zafran integrates with existing agents such as EDRs and firewall management tools to pull runtime data and configuration context.
Data sources and collection:
Vulnerability scanners, WAF, NGW and EDRs (Example integrations - Palo Alto Networks, CrowdStrike, Akamai, Zscaler, Tenable, Qualys, Rapid7), Zafran augments this with its own feed via Zafran Discover for real-time, vulnerability detection
Threat intelligence and risk signals from sources such as Mandiant and VulnCheck.
AppSec and code context - Connects infrastructure vulnerabilities to application code by ingesting SAST, DAST and SCA findings; Additional AppSec and configuration sources are noted for expansion
Prioritization and Risk Factors
Zafran moves beyond CVSS scoring by taking into account -
Runtime Context: Confirms whether vulnerable components are actually loaded and running in memory.
Internet Exposure: Assesses whether the on-prem or cloud asset is directly or indirectly exposed to the internet.
Threat Intelligence: Enriches findings with feeds from providers such as Mandiant and Recorded Future to determine if the issue is under active exploitation. EPSS scores are also taken into account.
Network and Exposure: Network reachability and control-path context to assess real exposure.
Existing control mitigations: Active control posture and configurations from tools like Palo Alto Networks, CrowdStrike, Zscaler, and Akamai with quantified risk reduction where controls are effective.
Mitigation options and impact: Alternative mitigations ahead of patch cycles using existing security defenses,
Control Gaps: Detect and alert on gaps misconfigurations of existing security controls, such as internet exposed assets without an EDR.
Zafran approaches prioritization by combining runtime presence, internet exposure, compensating controls, and active threat campaigns across hybrid environments.
Exploitability Assessment
Core differentiator: Runtime-informed approach to risk quantification and remediation. Zafran implements dynamic vulnerability risk scoring based on runtime verification, internet reachability, and the effectiveness of deployed controls such as EDRs, firewalls, and WAFs. Through its RemOps engine, Zafran bridges Security and IT by consolidating overlapping findings into unified tickets, auto-routing remediation tasks via Jira or ServiceNow, and tracking SLA-driven progress.
Evidence-based explainability: Validation occurs by confirming runtime execution of vulnerable components, assessing whether assets are internet-reachable, and correlating with evidence of active exploitation. It also quantifies how existing defenses from tools like CrowdStrike, Palo Alto Networks, and Zscaler reduce exposure, enabling evidence-backed exceptions and ROI reporting
Zafran demonstrates reclassification of critical CVEs based on runtime, reachability, and TI, with a process for downgrading false positives.
Remediation and True Risk State
Integrates natively with Jira and ServiceNow to operationalize remediation workflows
RemOps engine consolidates overlapping findings into unified “golden tickets” and auto-routes them to the right owners
Provides shared visibility across Security and IT, ensuring prioritization flows directly into structured remediation
Suggests control-based mitigations to reduce risk ahead of patch cycles
Offers step-by-step remediation guidance with estimated risk reduction tracked in the Mitigation Center
Zafran maintains a true risk state by downgrading criticality when appropriate.
Vision
Zafran positions itself as the unified exposure management platform, bridging vulnerability management, attack surface management, and SecOps, while advancing CTEM program maturity. The company is expanding the platform to natively support SCA, SAST, and DAST.
It is also making significant investments in Agentic AI for remediation as part of its roadmap and product vision. Zafran has recently introduced Agentic Remediation™ to combat the speed of AI-powered exploits, utilizing autonomous agents to enrich context and automate actions.
Analyst Take
There are the strengths and areas to watch in our opinion
Strengths:
Defense-aware, runtime-informed risk model: Analyzes runtime presence, internet reachability, and security controls already deployed to reclassify criticals and prove where risk is already mitigated.
Defense-in-place validation and quantified impact: Measures how tools like Palo Alto, CrowdStrike, and Zscaler reduce residual risk, enabling evidence-backed exceptions and reporting on ROI of controls.
Action-centric remediation operations (RemOps): Uses AI to collapse redundant CVEs into streamlined remediation items, suggests mitigations or patches, automatically creates Jira or ServiceNow tickets with SLAs, and tracks measurable risk reduction in the Mitigation Center.
Unified inventory and normalization: Aggregates, normalizes, and de-duplicates asset and vuln data across cloud and on‑prem into one central view.
Agentless-first with selective self-scanning: Leverages existing tools and agents to present a unified layer, augmenting with its own high-resolution checks where needed.
Areas to Watch:
Agentic Remediation: Agentic remediation is still maturing and will be a differentiator if execution is strong.
Customization: Ability for customers to add their own factors into the risk model was stated as in development, targeted by year‑end.
NOTE: This picture only represents vendors that were evaluated with in-depth product briefings, questionnaires and customer voices, for the purpose of this report. It is not meant to rank vendors by overall capabilities, but to highlight their specific strengths.
Other Notable Vendors
We didn’t do an in-depth product briefing with these vendors for this report but have interacted in some format or received information via questionnaires, shared assets or past briefings.
Armis
Armis Centrix is an exposure management platform built on a large-scale asset intelligence dataset and an early-warning threat research practice. It focuses on visibility and risk reduction by correlating vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, threat intelligence, and business context to help security teams prioritize and remediate risks before exploitation occurs.
The Armix Centrix platform takes in data from other Armis products (e.g. asset management and security, attack surface management, VMDR, and Prioritization and Remediation (VIPR Pro)) as well as other security tooling to provide views into compliance and business cyber exposure views.
Armis combines its global research arm (Armis Labs) with an Asset Intelligence Engine and an Early Warning system that identifies actively exploited CVEs, emerging campaigns, and fast-moving threats ahead of public industry disclosures. This combination enables customers to take preventive action before vulnerabilities become widely weaponized.
Mapping Armis’ Capabilities Against the Analysis Framework
Deployment
The platform is a SaaS-only solution at this time with support for hybrid customer environments for exposure analysis. Armis has its own native agentless and agent technologies for security and asset discovery, but also can also agentless ingest additional data from security tools.
Data Collection and Correlation
Draws from the Asset Intelligence Engine
Aggregates and enriches data from scanners, network traffic, and control systems to contextualize risk and ownership.
Uses Early Warning telemetry to detect exploitation activity before it appears on industry lists.
Prioritization and Risk Factors
Armis prioritizes exposures by combining exploitability, exposure, and business context:
Exploitability and exposure: Incorporates live exploitation activity, early-warning detections, and threat campaign intelligence.
Business context: Accounts for asset criticality, ownership, and operational importance to rank risk based on potential impact.
Vulnerability intelligence: Correlates actively exploited CVEs, vendor advisories, and chained exploit data into practical remediation guidance.
Domain coverage: Highlights risk across operational environments
Exposure Assessment
Armis differentiates itself through early detection and contextual reach:
The Early Warning capability maps global threat intelligence directly to customer environments, enabling proactive defenses before widespread exploitation.
Research-driven intelligence on malware and exploit chains provides practical verification and scoping during incident response.
Remediation and True Risk State
Armis integrates with existing workflow and automation tools to maintain accurate exposure states.
Workflow connectivity: Supports integrations with orchestration and ITSM platforms for coordinated response.
Supplies IOCs, and prioritized remediation actions when active exploitation is detected.
Progress management: Dashboards and reports track exposure reduction over time and help validate true risk posture.
Palo Alto Networks (Cortex Exposure Management)
Palo Alto Networks approaches vulnerability and exposure management as part of its broader platform strategy, unifying telemetry, policy, and workflow across Cortex Cloud and Prisma Cloud. Cortex Exposure Management extends the company’s XDR and SIEM foundation, ingesting first- and third-party findings to reduce duplication, correlate signals, and automate remediation within existing SOC workflows. The roadmap emphasizes compensating control modeling, agentic automation, and a consolidated data fabric that connects code, cloud, identity, endpoint, browser, and network enforcement points.
Deployment
Delivered as a cloud service within Cortex Cloud, Cortex Exposure Management is licensed as an add-on to Cortex XSIAM. The platform enables rapid time to value through prebuilt connectors and native PANW telemetry. Its roadmap is aligned toward a unified backend and interface experience that merges data security, ASPM, and exposure management into a single pane.
Data Collection and Correlation
Cortex ingests from external vulnerability scanners like Tenable and Qualys, complemented by a native PANW scanner for asset coverage gaps. It leverages telemetry from Cortex XDR agents, Enterprise Browser, and firewall/SWG infrastructure for runtime, identity, and network context. These data points are integrated into a unified data fabric within Cortex Cloud, enabling shared constructs such as assets, findings, and cases across PANW products.
Prioritization and Risk Factors
Prioritization goes beyond CVSS, focusing on deduplication and exploitability. The model incorporates threat intelligence, reachability, and runtime factors to highlight actionable vulnerabilities. The roadmap includes compensating control modeling and AI-driven automation to refine prioritization accuracy. In ASPM use cases, priority reflects impact and likelihood, integrating runtime exposure, sensitive data reach, and CI/CD context to promote prevention earlier in the lifecycle.
Exposure Assessment
A core differentiator is the platform’s breadth across endpoint, browser, network, SaaS, and cloud domains, enabling write-once policies enforced across multiple control points. ASPM connects to developer workflows to prevent new issues at source, while exposure management prioritizes the most impactful and fixable vulnerabilities for the SOC. Dashboards visualize ownership and prioritization funnels, aided by identity stitching that links findings to accountable teams.
Remediation and True Risk State
Bi-directional integrations with Jira, Slack, and ServiceNow route findings directly into team workflows. XSOAR automation supports contextual investigation, guided or reversible remediation, and synchronization of ticket status to maintain true risk state. Exposure reduction aligns with daily SOC operations, ensuring remediation activity and automation loops remain consistent across Cortex products.
Trend Micro (Vision One CREM)
Trend Micro’s Vision One Cyber Risk Exposure Management (CREM) platform focuses on proactive exposure assessment and risk reduction across identities, endpoints, cloud, and networks. CREM aggregates findings from Trend’s platform sensors and third-party sources to provide unified visibility and prioritization. The platform emphasizes exploitability-aware scoring, compensating controls, and measurable risk reduction, with roadmap investments in validation through adversarial exposure testing and a digital-twin approach to safely simulate attacks before production impact.
Trend Micro blends first-party telemetry with threat intelligence to prioritize remediation and, where possible, reduce risk quickly via virtual patching through host and network IPS. Agentless discovery for network infrastructure is a near-term roadmap feature intended to complement existing coverage. Validation capabilities are under active development to complete a full CTEM program lifecycle.
Mapping Trend Micro’s Capabilities Against the Analysis Framework
Deployment
CREM is delivered as part of the Trend Vision One SaaS platform, supporting hybrid environments across endpoints, cloud, identity, and networks.
Data Collection and Correlation
CREM leverages Trend’s native sensors and integrates external sources to build comprehensive asset and exposure context.
Data sources and collection:
First-party telemetry from endpoints and network sensors, cloud control planes, identity systems, and threat intelligence.
Third-party inputs via read-only APIs where applicable.
Risk index views in Vision One consolidate posture across all environments.
Prioritization and Risk Factors
Trend’s vulnerability impact scoring extends beyond CVSS to include:
External severity and exploit likelihood from EPSS, known exploited vulnerabilities, and Trend threat intelligence.
Internet exposure and reachability, assessing blast radius through cloud and network context.
Control posture and the presence or effectiveness of IPS/EDR and other compensating controls, enabling virtual patching where appropriate.
Business context and ownership to align work with SLAs.
Unified risk scoring across CVE and non-CVE issues for an exposure-centric view.
Exploitability Assessment
Trend Micro differentiates itself through tight coupling of prioritization with IPS-backed exploit detection and virtual patching to mitigate risk ahead of patch windows. A digital-twin based Adversarial Exposure Validation (AEV) capability is in development to safely validate attack paths and factor real exploitability into scoring.
Remediation and True Risk State
CREM supports both reporting and operational workflows to drive closure.
Reports and auditability: Risk dashboards and reports align to measurable reduction outcomes and executive visibility.
Managing workflows: The platform generates prioritized remediation items enriched with context and justification for downstream ITSM systems.
Enforcing remediation: Virtual patching and automated playbooks reduce exposure while permanent fixes are scheduled. Continuous state re-sync prevents stale findings.
Wiz Security
Wiz approaches vulnerability and exposure management from its CNAPP foundation, extending its well-known cloud security graph into a unified exposure management layer. Following its 2025 integration of the acquired Dazz technology, Wiz now combines vulnerability discovery, aggregation, and remediation orchestration into a single platform that centralizes all risk data native or external, within its “Security Graph.”
Wiz’s model unifies findings from both Wiz-native detections and some external sources (Qualys, Tenable) into one normalized, deduplicated data lake. This also scans code repositories, ensuring code to cloud lifecycle that goes from discovery and prioritization to ticket creation and fix verification, all inside the Wiz console.
Mapping Wiz’s capabilities against the DDPER framework
Deployment
Wiz Exposure Management is part of Wiz Advanced, offered primarily as a SaaS platform with native integrations into major clouds (AWS, Azure, GCP). It supports hybrid environments through the same Wiz sensors used for CNAPP visibility and can also ingest data via API from on-premises tools. No new agents are required, customers can connect existing scanners or rely solely on Wiz’s agentless architecture.
Data Collection and Correlation
Wiz’s Security Graph remains the foundation of data correlation. It ingests and models every asset, vulnerability, and identity relationship across the cloud, infrastructure, and application layers, adding external telemetry from third-party scanners, code analysis tools, and CMDBs.
Data sources include:
Wiz native scanning (cloud, container, and code)
Third-party scanners (Qualys, Tenable)
AppSec tools (Checkmarx, Veracode, Snyk, Invicti)
Ticketing and CMDB systems (ServiceNow, Jira)
Threat intelligence and exploit feeds (EPSS, KEV, Wiz Threat Center)
Wiz deduplicates vulnerabilities across sources, correlates them to their cloud assets, and enriches them with identity, network reachability, and data sensitivity. Each issue becomes part of a connected context graph representing exposure across environments.
Prioritization and Risk Factors
Wiz goes beyond CVSS scoring by taking into account -
Reachability: Determines whether the vulnerable asset is internet-exposed or internally reachable.
Attack path analysis: Extends Wiz’s signature graph logic to show how multiple exposures combine into real attack paths.
Data sensitivity and business context: Connects vulnerabilities to data classification, production workloads, and CMDB-mapped owners.
Identity context: Evaluates whether privileges, IAM misconfigurations, or excessive permissions make an issue exploitable.
Threat intelligence: Integrates Wiz Threat Center research, KEV, and EPSS likelihood to reflect live exploit conditions.
Policy-based priorities: Allows organizations to define compliance-driven SLAs (e.g., FedRAMP or internal 30-day rules) within the same prioritization model.
Exploitability Assessment
Wiz extends its cloud-native risk and exposure analysis beyond Wiz-discovered issues to imported findings, merging cloud posture and external vulnerabilities into one attack-path visualization. Each issue can be traced through the security graph to show its reachability, connected data, and potential exploit chain.
A differentiator is the Security Graph-driven de-duplication and correlation, which enriches imported vulnerabilities with Wiz’s own runtime context turning isolated scanner data into full attack-path insights.
Remediation and True Risk State
Wiz automates remediation through bi-directional integration with ServiceNow, Jira, and CI/CD systems.
Vulnerabilities are automatically routed to the correct project or team based on CMDB mapping.
Each ticket carries the complete context (asset, path, severity, owner, and fix guidance).
Closed tickets trigger verification scans to confirm resolution, updating the true risk state dynamically.
Remediation playbooks and policies ensure consistent workflows across all asset types, whether the issue came from Wiz or an external scanner.
Vision
Wiz’s long-term goal is to make the Security Graph the control plane for all enterprise exposure management. The company aims to unify vulnerability, posture, and identity data from any source into one consistent model, where remediation workflows are automated and prioritized by real exploitability. Its roadmap includes deeper AI-driven prioritization, expanded code-to-cloud correlation (SAST, SCA, DAST), and generative guidance for remediation and reporting.
Zscaler Exposure Management
Zscaler aims to address exposure and risk management by bringing everything into its security data fabric - security findings, security controls, assets, etc - to contextualize, prioritize, and ultimately, automate the remediation and mitigation of cyber risk.
Deployment and Data Ingestion
The platform is SaaS only but supports customers’ hybrid environments for its CTEM platform’s analysis.
Zscaler ingests data from pre-built data connections to security and IT systems and also pulls in data from JSON, XML, CSV, ZIP and other formats. Data ingested is stored in Zscaler’s data fabric for security to be harmonized, de-duplicated, correlated, and enriched. While Zscaler’s Exposure Management platform is independent from other Zscaler’s services, it can be enriched with additional telemetry if additional Zscaler services are part of an organization’s toolset.
Risk Factors
Zscaler’s CTEM platform takes the following risk factors into account
External Exposure: Identifies assets exposed to the internet, raising their risk profile.
Uses customer-provided IP ranges to determine which assets are behind a firewall versus open to the internet.
Coverage Gap: Detects coverage gaps by comparing data across tools like CrowdStrike, Qualys, and CMDB.
Business Context: Incorporates environmental context through tags or labels
Adjusts risk scores based on asset role, such as differentiating between dev and production environments.
Sensitive Data Exposure: Ingests insights from DSPM tools to locate PII, financial, or regulated data. Detects exposure directly or by analyzing user access to sensitive systems.
Asset Criticality: Integrates with the CMDB to determine business importance. Prioritizes “crown jewel” and critical applications in risk calculations.
User Behavior Patterns: Applies behavior analytics to strengthen risk scoring. Factors in indicators like repeated phishing test failures to identify higher-risk users.
Zscaler also allows an organization to customize the model according to their needs.
Remediation
Bi-directional ticket reconciliation with ticketing systems and CMDBs
Reporting/dashboard creation capabilities.
Integration with the Zscaler Zero Trust platform enables enforcement actions based on risk data.
Vision
Zscaler’s vision is to provide a single, holistic platform that breaks down silos and gives organizations a complete view of their assets and exposures. This platform would automatically prioritize risk by criticality and be part of a feedback loop between Zero Trust Exchange (ZTA) and a SecOps platform (which includes both exposure and threat management) to automate risk reduction.
Strengths:
Customizable Risk Weighting: Ability to customize risk weighting for specific organizational needs
Automation & Remediation Workflow: Tailored remediation plans with strong automation capability to drive down MTTR but also keep other relevant systems and teams up to date as exposure changes.
Zero Trust Integration: Beyond notification to action to minimize risk
General Companies
We wanted to make sure to include some other potential exposure management vendors in the report even though we didn’t do an in-depth briefing on their platform or gain any interaction from them pertaining to this.
Qualys
Qualys remains the one of the prominent vulnerability scanning platforms, with deep enterprise penetration and reliability built over decades. Its scanning infrastructure, compliance modules, and integrations make it a cornerstone of many vulnerability management programs. However, we are yet to see them evolve into a full fledged risk prioritization and exposure management platform.
While Qualys is moving toward risk-based vulnerability management (RBVM) through the introduction of its VMDR (Vulnerability Management, Detection, and Response) suite, the product still emphasizes breadth over contextual depth. It excels in coverage and reporting but lags in the operational integration and exploitability validation that characterize modern exposure management platforms.
In one of our brief calls with them, we saw their intention to move towards exposure management and prioritization by taking into account factors beyond CVSS scores. We do not have a full list of risk factors that are taken into account, but one unique factor they presented was the ability to add a monetary value (in dollars) as business context into the platform. Emphasizing that tying a monetary value as a factor increases its prioritization. While the idea is interesting, we wonder if businesses would be able to constantly sync monetary values back to a risk management platform.
In 2025’s exposure management context, Qualys is a foundational system of record but not the decision engine. Many modern vendors (Astelia, Seemplicity, Zafran) use Qualys data as a feed rather than a replacement, illustrating its evolution from the “core platform” to a “data provider” in the exposure ecosystem.
Rapid7
Rapid7 has historically differentiated itself by combining vulnerability management with a strong operational layer, tying scanning, analytics, and automation through InsightVM, InsightIDR, and InsightConnect. Its appeal among mid-market customers came from usability and faster time-to-value compared to Qualys or Tenable. However, as exposure management moves toward unified and AI-assisted prioritization, Rapid7’s platform still operates as a modular stack rather than a cohesive exposure fabric.
The firm’s “Insight” ecosystem provides visibility, but its data model remains detection-centric rather than outcome-oriented, meaning it’s optimized for identifying issues, not dynamically validating or reducing exposure. Rapid7’s recent consolidation efforts aim to unify its telemetry across vulnerability, detection, and response, but the approach feels evolutionary rather than transformative.
In exposure management terms, Rapid7 represents the “bridge generation”, transitioning from legacy VM toward exposure orchestration but not fully achieving it yet.
Tenable
Tenable pioneered the category with Nessus and still commands strong brand equity, but its evolution has been incremental. The company has added layers like RBVM capabilities, OT/IoT scanning, and cloud connectors but these often exist as separate modules rather than a unified risk engine.
Its Tenable One platform represents a genuine effort to pivot from traditional scanning toward exposure management, offering asset inventory correlation and analytics across hybrid environments. However, its reliance on asset-based aggregation and periodic assessment limits its responsiveness to the dynamic nature of threats in 2025.
Tenable’s strength lies in governance and audit-driven environments, where its compliance-first DNA continues to resonate. Yet, its risk modeling and exploit validation trail behind modern platforms like XM Cyber and Zafran, which apply real-time attack-path analytics and control-state verification.
In the context of vulnerability risk and exposure management, Tenable’s positioning is more of a risk dashboard than an exposure engine. Many enterprises like Seemplicity or Astelia, now use Tenable as one of several feeds ingested into orchestration or validation layers, rather than as the central decision layer.
Vulnerability Risk and Exposure Management - SACR Prediction
Looking ahead we see the evolution of vulnerability and risk management platforms in two directions
Aggregators expanding in-house scanning
Aggregator-style platforms or unified vulnerability management platforms, which today focus on normalizing and correlating data from third-party scanners, CNAPPs, and posture tools will increasingly introduce in-house scanning capabilities. This trend addresses the needs of organizations that either:
Lack an existing vulnerability management stack, or
Want a single-source-of-truth without relying on external data dependencies.
Expect vendors that have historically positioned themselves as “aggregator and unified VM layers” to develop lightweight agentless scanning modules for basic asset discovery and vulnerability enumeration. These capabilities will complement their correlation and remediation engines, giving them dual value as both aggregator and source of vulnerability intelligence.
Pure-Play Platforms moving up the stack
Meanwhile, pure-play vulnerability and exposure platforms that already provide native scanning and posture management will continue expanding upward into contextual analytics and remediation orchestration. They will evolve from point scanners into autonomous exposure management suites capable of:
Correlating vulnerability, identity, data posture and network context;
Going deeper on runtime exploitability to challenge the aggregators; and
Investing heavily in agentic AI for automating remediation workflows
This evolution will be driven by customer demand for outcome-based risk reduction metrics, not volume-based vulnerability counts.
Conclusion
Vulnerability management and the need for reducing alert fatigue by prioritizing true risk continues to be a core requirement for organizations. The traditional KPIs of CVSS scores and vulnerability counts no longer represent success; instead, measurable risk reduction, exploitability validation, and remediation velocity define modern maturity.
The convergence of historically distinct categories VM, RBVM, ASM, CAASM, ASPM, CNAPP, and BAS, with an evolution beyond CTEM capabilities - under the modern risk and exposure management umbrella reflects how practitioners and threat actors now operate. The evolution described in this report signals that exposure management is becoming the connective tissue between asset intelligence, control validation, and remediation operations.