By Jonathan Montagu, CEO of HotSpot Therapeutics, as part of the From The Trenches feature of LifeSciVC
In the perpetual and never-ending race by the healthcare sector to unearth new approaches and therapeutics to address disease, one area in which we are seeing novel innovation is in the targeting of transcription factors.
While the successful therapeutic targeting of transcription factors is a relatively new undertaking by industry, these proteins themselves are nothing new. Transcription factors are well-known entities – they are the hairclip-shaped molecules that when activated, travel into to the nucleus, grab onto DNA, and drive the transcription of genes into proteins.
Moreover, transcription factors have been shown to play a role in a broad range of diseases, ranging from cancer to autoimmune disease, to cardiovascular disease, to neurological disorders. The roles of certain transcription factors in disease pathogenesis have been well-elucidated and scientifically substantiated:
- Robust genetic validation: Through reviewing genome-wide association studies, we are able to unearth correlations between upregulated levels of certain transcription factors across patients with certain diseases.Substantial biological validation: As transcription factors play central roles in the up-/down-regulation of distinct signaling cascades, we have the ability to look to other pathway regulators, whether that be upstream or downstream, to understand the degree to which a given pathway’s modulation has on disease.
Given this ever-increasing body of evidence, why is it that for so long, they have not been the focus of drug discovery? The short answer is that it has not been for lack of effort – an understanding of transcription factors themselves, and how they are regulated, helps explain.
Traditional drug discovery is largely “active-site directed” – meaning inhibitors of proteins have historically been designed to latch onto the active, or catalytic, sites of proteins, thereby blocking their ability to undertake further action or function. And herein lies the challenge for transcription factors! Lacking active sites entirely, transcription factors are instead largely regulated by post-translational modification, which in turn impacts changes in conformation, behavior, and interaction with other proteins.
However, in recent years, huge leaps have been made in drug discovery – ranging from novel technologies unearthing new techniques for small molecule development to new modalities like targeted protein degradation – that are beginning to open the door to a promising wave of transcription factor-directed therapeutic candidates.
One area of interest is that of oncology, where growing evidence has shown the role that transcription factors play in driving various cancers. C4 Therapeutics is one company leading the therapeutic application of protein degradation, a process by which target proteins are “tagged” with ubiquitin to cause degradation of the target. C4’s leading program, cemsidomide, is focused on targeting IKZF1/3, transcription factors that drive cancer cell proliferation and survival in multiple myeloma and Non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Other companies, like Vividion Therapeutics and Flare Therapeutics, are applying new approaches to small molecule drug development to unearth previously undetectable druggable pockets that play important roles in transcription factor activation, with clinical-stage programs in distinct cancer settings.
Another promising area of scientific advancement is in the treatment of autoimmune disease, where numerous biotechnology companies are deploying innovative techniques to target transcription factors that are directly implicated in disease. Companies like Kymera Therapeutics and Nurix Therapeutics are applying their respective protein degradation drug discovery platforms to the development of transcription factors including STAT6, a regulator of the IL-4/IL-13 pathway that is implicated in a range of Th2-mediated allergic diseases. Another company pursuing a novel approach to transcription factor targeting is Recludix Pharma, which is leveraging its SH2 domain-directed platform to selectively target STAT6 and STAT3, another transcription factor in the STAT family that is implicated in Th17-driven autoimmune disease.
At HotSpot, we too have homed in on the transcription factor target class as an exciting application for our allosteric drug discovery platform. Our platform allows us to identify and unlock the control mechanisms that exert functional influence on a protein’s activity – a technology ideally suited to the targeting of transcription factors. Through our platform, our early research has enabled dozens of transcription factors implicated across a wide range of disease, from immunology, to oncology, and beyond.
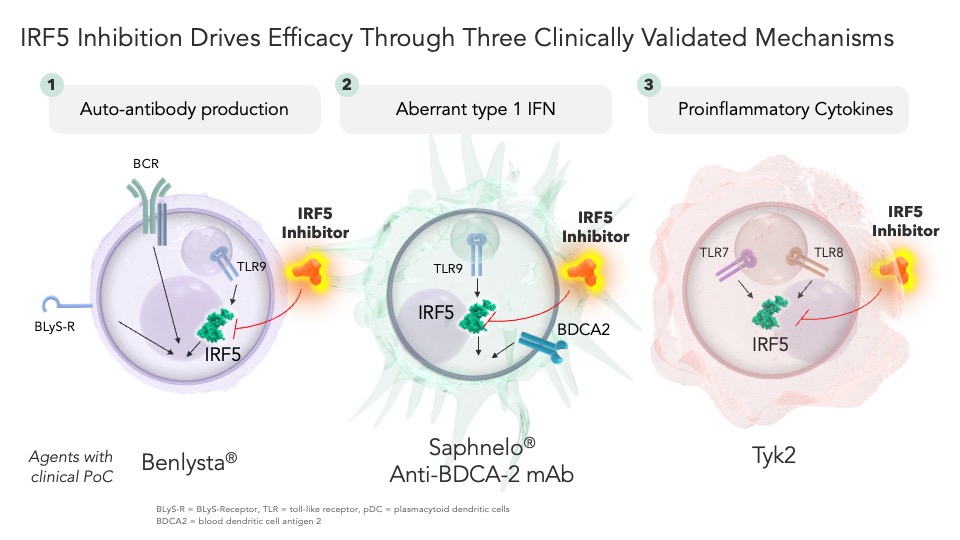
Leading our pipeline is our IRF5 inhibitor program, a transcription factor that functions as a master regulator of innate immunity. IRF5 utilizes a triple-mechanism approach, impacting autoantibody production, interferon levels, and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines:
IRF5 has been shown to have striking genetic validation in numerous diseases, including systemic lupus erythematosus, Sjögren’s syndrome, rheumatoid arthritis, and other autoimmune disorders. Moreover, each of the signaling pathways regulated by IRF5 have varying degrees of clinical validation, with drugs either approved or producing promising clinical data that play a role in regulating upstream or downstream factors. Given this profound genetic, biologic, and clinical validation, it’s no surprise that an IRF5 inhibitor has been long sought-after by industry – yet the unique challenges presented by IRF5 have led to failure after failure.
At HotSpot, our platform has uniquely enabled the discovery and development of highly potent and selective small molecule inhibitors of IRF5, which are in turn yielding compelling in vivo data proving out the triple-mechanism effects of an IRF5 inhibitor. As we progress our program through pre-clinical development and into the clinic, we aim to marry this activity with a favorable tolerability profile and convenient oral dosing to bring forward a highly differentiated and convenient treatment option for patients.
We look forward to the continued advancement not only of our own IRF5 program, but also to the collective advancement of this novel class of therapies with broad-ranging potential across disease. As this wave of programs progress into and through clinical development, we’ll begin to uncover if these innovative drug discovery technologies are finally able to scratch the surface of the therapeutic promise of targeting the transcription factor class – which, in the long run, has the potential to yield many more waves in the years to come.
The post A New Wave of Therapeutic Innovation Through Targeting Transcription Factors appeared first on LifeSciVC.