4 Key Insights for Scaling LLM Applications (Sponsored)
LLM workflows can be complex, opaque, and difficult to secure. Get the latest ebook from Datadog for practical strategies to monitor, troubleshoot, and protect your LLM applications in production. You’ll get key insights into how to overcome the challenges of deploying LLMs securely and at scale, from debugging multi-step workflows to detecting prompt injection attacks.
This week’s system design refresher:
How Java Works
How Gitflow Branching Works?
Become an AI Engineer | Learn by Doing | Cohort Based Course
The Life of a Redis Query
6 Steps to Create a New AI Model
How Java Works
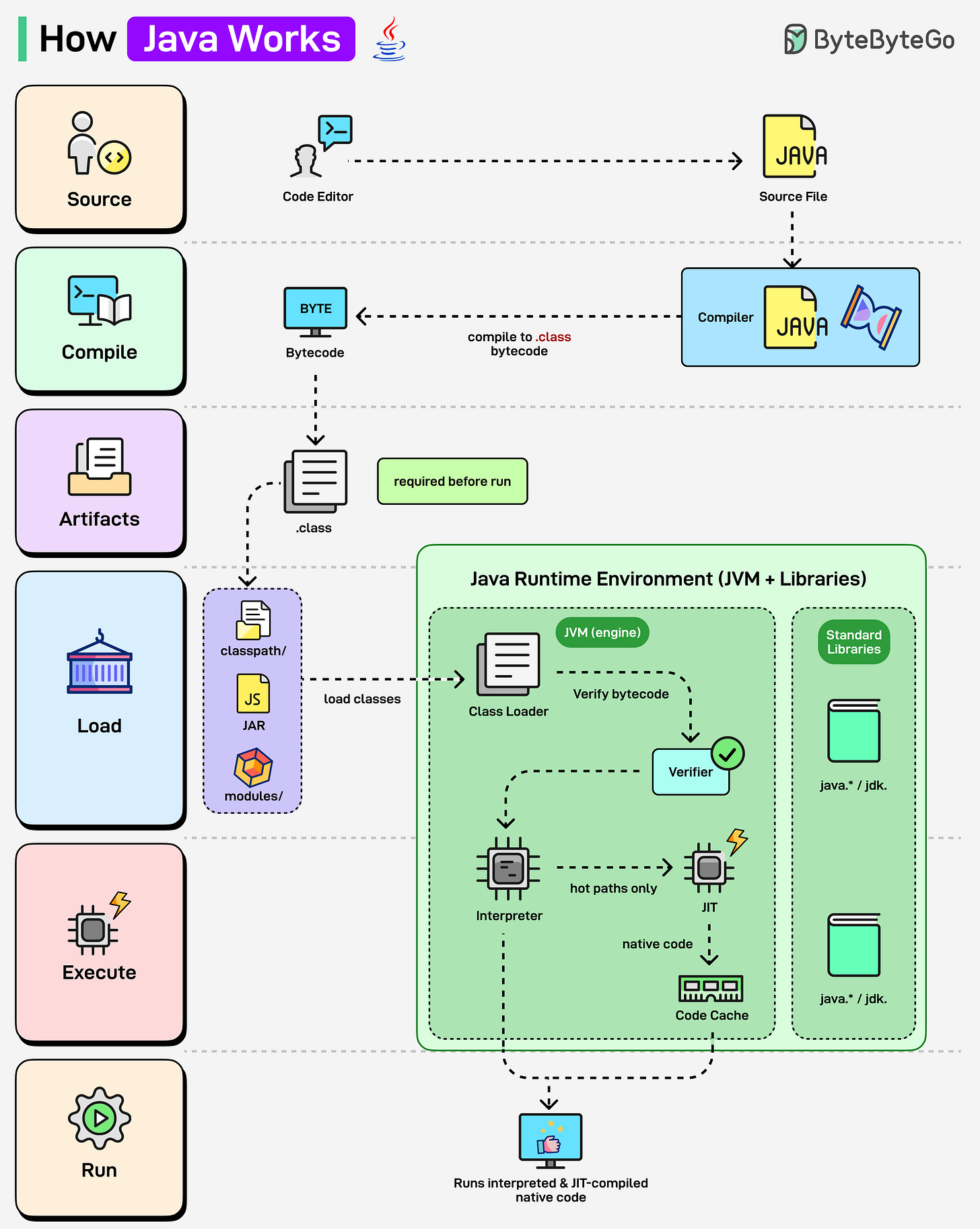
Ever wondered what happens behind the scenes when you run a Java program? Let’s find out:
Java (JVM Runtime):
Java source code (.java) is compiled into .class bytecode using javac.
The Class Loader loads bytecode into the Java Runtime Environment (JVM).
Bytecode is verified and executed.
JVM uses both an Interpreter and a JIT Compiler, frequently used code (hot paths) is converted into native machine code, making Java faster.
Over to you: For large-scale systems, do you still see Java as the go-to language?
CodeRabbit: Free AI Code Reviews in CLI (Sponsored)
CodeRabbit CLI is an AI code review tool that runs directly in your terminal. It provides intelligent code analysis, catches issues early, and integrates seamlessly with AI coding agents like Claude Code, Codex CLI, Cursor CLI, and Gemini to ensure your code is production-ready before it ships.
Enables pre-commit reviews of both staged and unstaged changes, creating a multi-layered review process.
Fits into existing Git workflows. Review uncommitted changes, staged files, specific commits, or entire branches without disrupting your current development process.
Reviews specific files, directories, uncommitted changes, staged changes, or entire commits based on your needs.
Supports programming languages including JavaScript, TypeScript, Python, Java, C#, C++, Ruby, Rust, Go, PHP, and more.
Offers free AI code reviews with rate limits so developers can experience senior-level reviews at no cost.
Flags hallucinations, code smells, security issues, and performance problems.
Supports guidelines for other AI generators, AST Grep rules, and path-based instructions.
How Gitflow Branching Works?
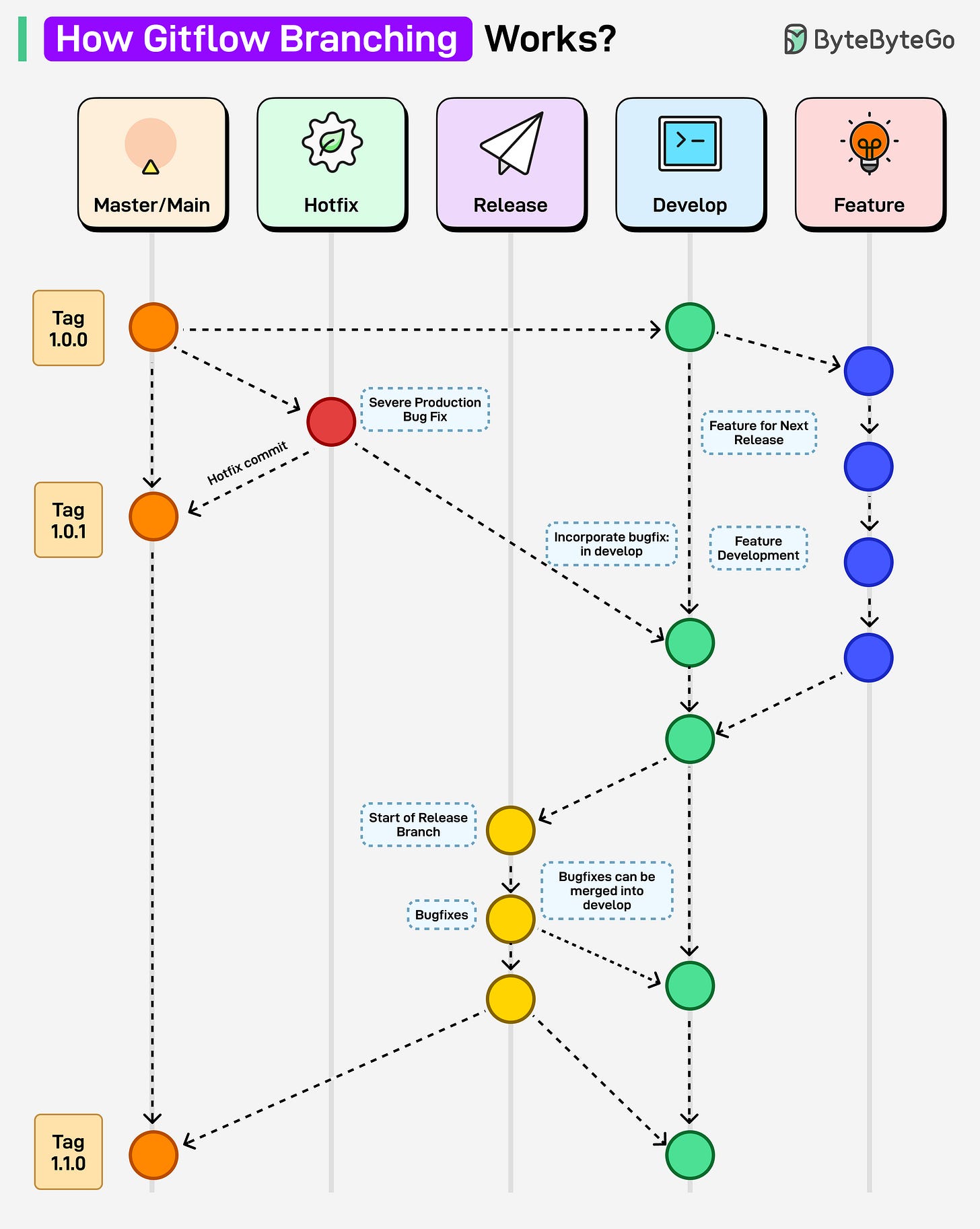
Gitflow branching strategy is a Git workflow that organizes development into dedicated branches for features, releases, hotfixes, and the main production line. It is an ideal Git branching strategy for projects with regular versioned deployments.
Here’s how it works:
1. Development starts on the develop branch, where new features are integrated.
2. Each feature branch is created from develop and merged back once the feature is complete.
3. When preparing for a release, a release branch is created from develop for final bug fixes.
4. Release branches are merged into main (for production) and back into develop to keep a consistent history.
5. For urgent fixes, a hotfix branch is created directly from main, then merged back into both main and develop.
Over to you: Which Git branching strategy do you follow in your project?
Help us Make ByteByteGo Newsletter Better
TL:DR: Take this 2-minute survey so I can learn more about who you are,. what you do, and how I can improve ByteByteGo
Become an AI Engineer | Learn by Doing | Cohort Based Course
After months of preparation, I’m thrilled to announce the launch of the very first cohort of Becoming an AI Engineer. This is a live, cohort based course created in collaboration with best-selling author Ali Aminian and published by ByteByteGo.
This is not just another course about AI frameworks and tools. Our goal is to help engineers build the foundation and end to end skill set needed to thrive as AI engineers.
Here’s what makes this cohort special:
• Learn by doing: Build real world AI applications, not just by watching videos.
• Structured, systematic learning path: Follow a carefully designed curriculum that takes you step by step, from fundamentals to advanced topics.
• Live feedback and mentorship: Get direct feedback from instructors and peers.
• Community driven: Learning alone is hard. Learning with a community is easy!
We are focused on skill building, not just theory or passive learning. Our goal is for every participant to walk away with a strong foundation for building AI systems.
If you want to start learning AI from scratch, this is the perfect time to begin.
The Life of a Redis Query
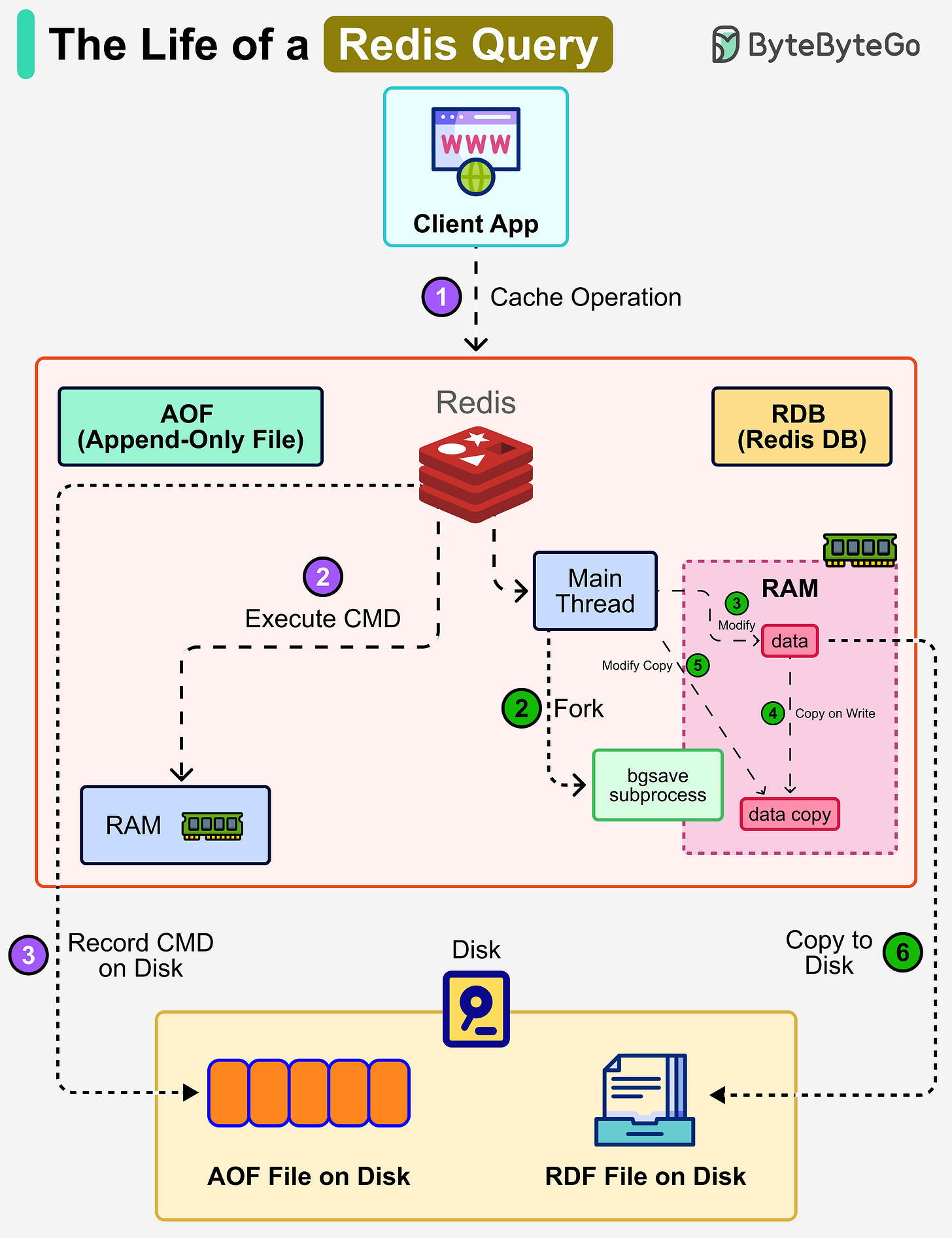
Redis is an in-memory database, which means all data lives in RAM for speed. However, if the server crashes or restarts, data could be lost. To solve this problem, Redis provides two persistence mechanisms to write data to disk:
AOF (Append-Only File)
When a client sends a command, Redis first executes it in memory (RAM). After that, Redis logs the command by appending it to an AOF file on disk. This ensures every operation can be replayed later to rebuild the dataset. Since the command is executed first and logged afterward, writes are non-blocking. The recovery process uses the event log to replay the recorded commands.
RDB (Redis Database)
Instead of writing every command, Redis can periodically take snapshots of the entire dataset.
The main thread forks a subprocess (bgsave) that shares all the in-memory data of the main thread. The bgsave subprocess reads the data from the main thread and writes it to the RDB file.
Redis uses copy-on-write. When the main thread modifies data, a copy of the data is created, and the process works on that so that writes don’t get blocked. The snapshot is then written as an RDB file on disk, allowing Redis to quickly reload the snapshot into memory when needed.
Mixed Approach
In production, Redis often uses both AOF and RDB. RDB provides fast reloads with compact snapshots. AOF guarantees durability by recording every operation since the last snapshot.
Over to you: Have you used Redis in your project?
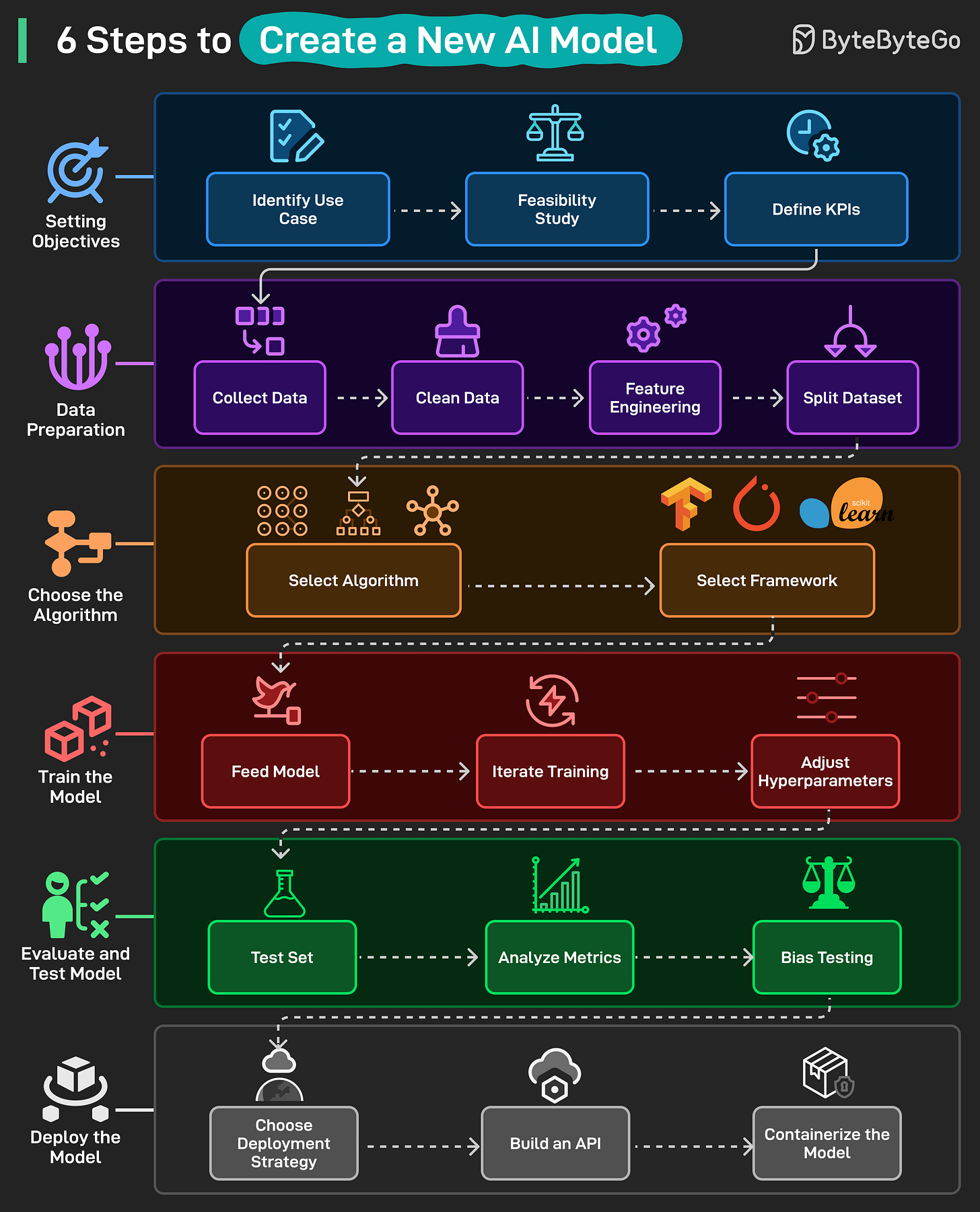
6 Steps to Create a New AI Model
Setting Objectives: Define the problem to be solved by the AI model by identifying use cases, checking feasibility, and setting clear KPIs for success.
Data Preparation: Gather and clean raw data, engineer useful features, and split the data into training, validation, and test sets.
Choose the Algorithm: Pick the right algorithm for your problem and select a framework (for example, TensorFlow, PyTorch, Sci-kit Learn.
Train the Model: Feed data into the model, iterate training, and tune hyperparameters until performance improves.
Evaluate and Test Model: Test on unseen data, analyze performance metrics, and check for bias or unfair outcomes.
Deploy the Model: Select a deployment strategy, build an API, and containerize the model for production use.
Over to you: Which other step will you add to the list?
SPONSOR US
Get your product in front of more than 1,000,000 tech professionals.
Our newsletter puts your products and services directly in front of an audience that matters - hundreds of thousands of engineering leaders and senior engineers - who have influence over significant tech decisions and big purchases.
Space Fills Up Fast - Reserve Today
Ad spots typically sell out about 4 weeks in advance. To ensure your ad reaches this influential audience, reserve your space now by emailing sponsorship@bytebytego.com.