Today, we’re introducing a new integration between GitHub and JFrog that connects your source code and your attested binaries in one secure, traceable workflow.
For developers who often find themselves jumping between multiple tools to figure out which commit produced which artifact — or piecing together results from separate security scans for code and binaries — this integration can save time and effort, centralizing everything you need all in one place.
Below, we’ll dig into why the GitHub and JFrog integration is important, how it works, and how you can start using it today.
Why we built the GitHub and JFrog integration
Modern software delivery is a supply chain. Your source code, build pipelines, and production artifacts are all links in that chain — and every link needs to be secure, traceable, and automated. Likewise, any weak link is a point of ingress for bad actors to gain access to data that should remain private and secure.
But keeping this complete supply chain secure is challenging for developers who have numerous (and continually growing) responsibilities. When we talked to teams shipping at scale, we kept hearing the same pain points:
- “We lose traceability once the build leaves GitHub.”“Security scanning is split between multiple systems, and we have to reconcile results manually.”“Our CI/CD pipelines feel stitched together instead of seamless.”
To address these issues, we worked closely with JFrog’s engineers to design a workflow where the commit that triggers a build is cryptographically linked to the artifact it produces, security scanning happens automatically and in context — providing the vulnerability scan attestations located in JFrog Evidence, and publishing and promoting artifacts, in compliance with an organization’s policies, is just another step in your GitHub Actions workflow, not a separate process.
Our goal: to remove friction, reduce risk, and give developers more time to focus on building features instead of managing handoffs.
The integration we’re announcing today unlocks a seamless experience that lets you:
- Run unified security scans, prioritizing Dependabot alerts based on production context from JFrog.Publish and promote artifacts using policy-based gating of artifact promotion.Automatically have all attestations created on GitHub (provenance, SBOM, custom attestations) ingested into JFrog evidence and associated with the build artifact.
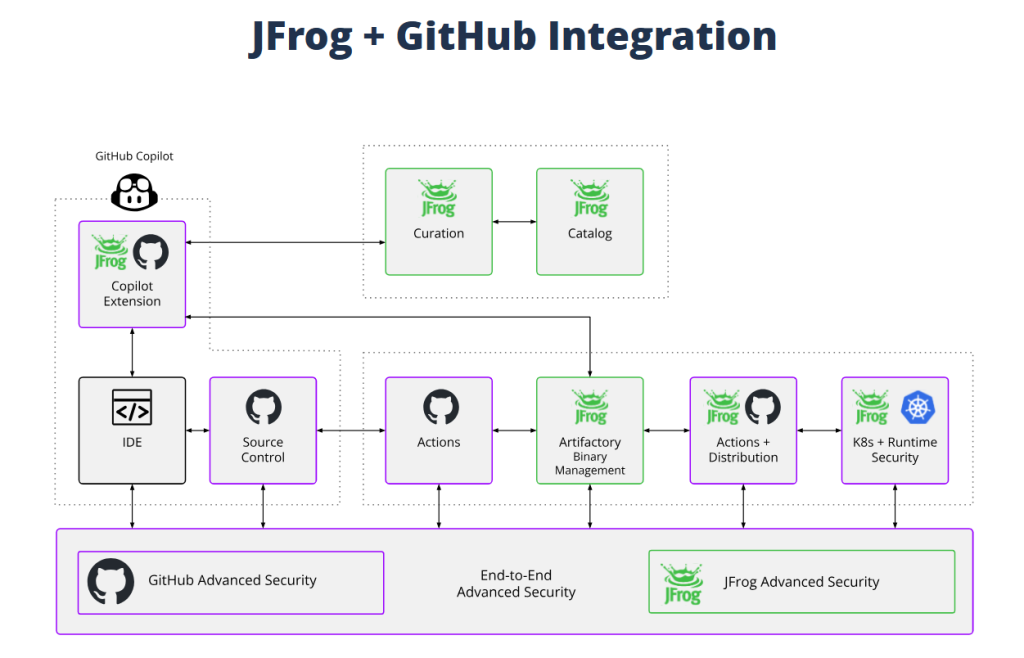
Here’s how it works
The integration connects GitHub’s developer platform with JFrog’s software supply chain platform using secure authentication and build metadata.
Here’s the flow:
- Push code to GitHub.Build and test with GitHub Actions.Link commits, builds, and artifacts for full lifecycle visibility.Publish artifacts to Artifactory automatically.Scan code with GitHub Advanced Security and artifacts with JFrog Xray.
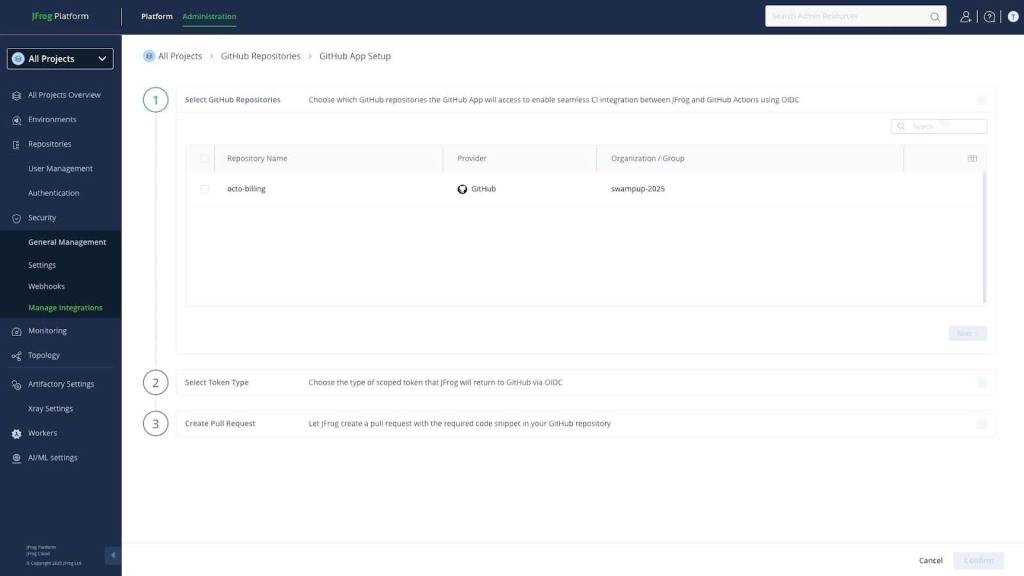
Setting it up
- Enable the GitHub integration in JFrog Artifactory by navigating to Administration → General Management → Manage Integrations → GitHub. Toggle “Enable GitHub Actions” and authenticate your GitHub organization. Select your token type. Then create a pull request.
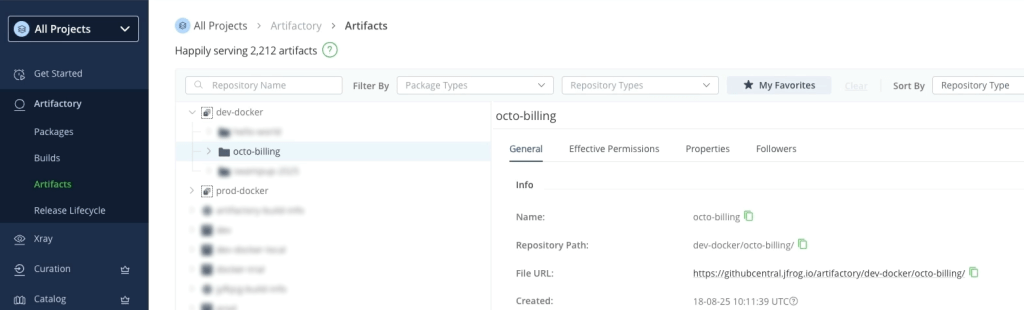
- Trigger a build of your GitHub Actions workflow to build the artifact and generate the attestation. Make sure that your GitHub Actions workflow is using the ‘jfrog/jfrog-setup-cli’ and ‘actions/attest-build-provenance’ actions.
- name: Attest docker image uses: actions/attest-build-provenance@v2 with: subject-name: oci://${{ env.JF_REGISTRY }}/${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }} subject-digest: ${{ steps.build-and-push.outputs.digest }}Here’s an example of a workflow that you can use to generate the attestation and push it to Artifactory:
name: Build, Test & Atteston: push: branches: - main env: OIDC_PROVIDER_NAME: [...] JF_URL: ${{ vars.JF_URL }} JF_REGISTRY: ${{ vars.JF_REGISTRY }} JF_DOCKER_REPO: [...] IMAGE_NAME: [...] BUILD_NAME: [...]jobs: build-test-deploy: runs-on: ubuntu-latest permissions: contents: read packages: write attestations: write # Required for attestation id-token: write # Added for OIDC token access steps: - name: Checkout code uses: actions/checkout@v5 - name: Install JFrog CLI id: setup-jfrog-cli uses: jfrog/setup-jfrog-cli@v4.5.13 env: JF_URL: ${{ env.JF_URL }} with: version: 2.78.8 oidc-provider-name: ${{ env.OIDC_PROVIDER_NAME }} - name: Docker login uses: docker/login-action@v3 with: registry: ${{ env.JF_REGISTRY }} username: ${{ steps.setup-jfrog-cli.outputs.oidc-user }} password: ${{ steps.setup-jfrog-cli.outputs.oidc-token }} - name: Set up Docker Buildx uses: docker/setup-buildx-action@v3 - name: Build and push Docker image id: build-and-push uses: docker/build-push-action@v6 with: context: . push: true tags: ${{ env.JF_REGISTRY }}/${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }}:${{ github.run_number }} build-args: ${{ env.BUILD_ARGS }} - name: Attest docker image uses: actions/attest-build-provenance@v2 with: subject-name: oci://${{ env.JF_REGISTRY }}/${{ env.IMAGE_NAME }} subject-digest: ${{ steps.build-and-push.outputs.digest }}- Once the build has run and the attestation has been generated, it will push the artifact to the JFrog Artifactory staging repo. The artifact is now ready to be validated.
- Once the artifact has been verified, confirming that a valid GitHub-signed provenance matches the trusted conditions (for example the issuer, repo, workflow, branch), on the policy passing, JFrog can automatically promote the attestation from the dev environment to the production environment. Now that artifacts have been promoted to production, Dependabot continues scanning its source repository, looking for dependencies and vulnerabilities. When a critical CVE is discovered, administrators will receive an alert of the security threat.
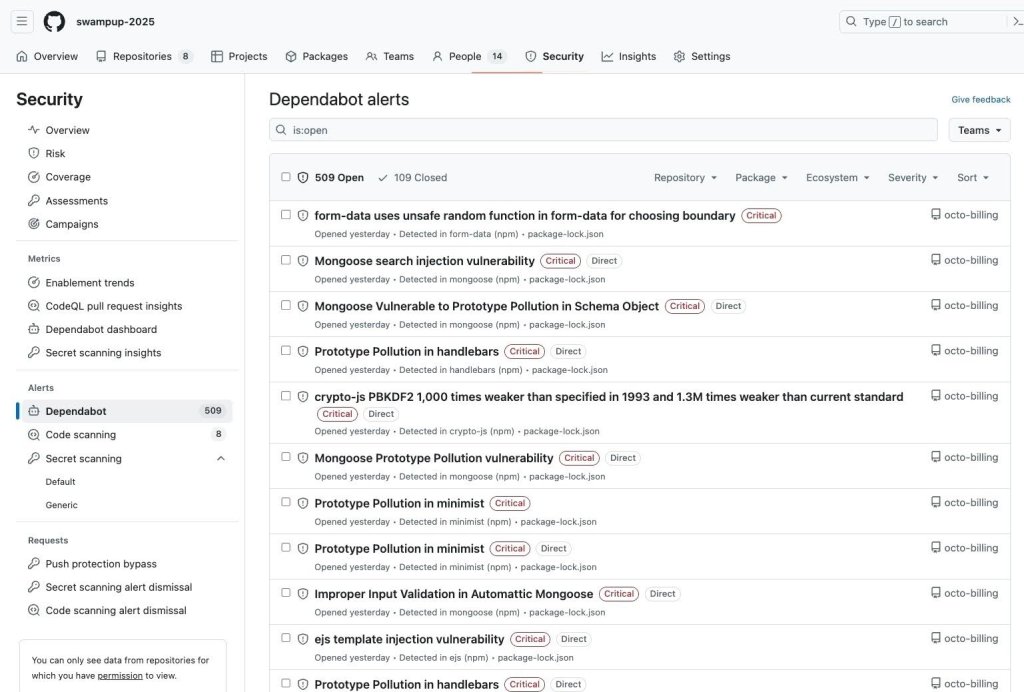
- To find the alerts and vulnerabilities for artifacts that made it to production, we can filter with the following tag:
artifact-registry:jfrog-artifactory.With this integration enabled, artifact lifecycle data is automatically pushed from JFrog to GitHub using GitHub’s new artifact metadata API. When an artifact is promoted to production in JFrog Artifactory, JFrog will automatically notify GitHub about the promotion, so that the artifact is picked up with the new Dependabot filter.
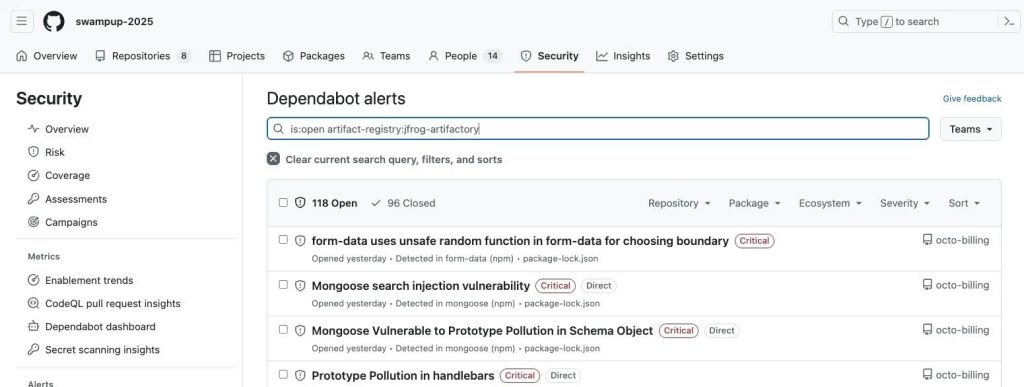
- Once an alert has been identified, it can be remediated using the suggested dependency update, which then allows you to rebuild and redeploy with fresh provenance.
To get the most out of using GitHub and Jfrog Artifactory, here are a few best practices:
- Use OIDC to avoid long-lived credentials in your workflows.Automate promotions in Artifactory to move artifacts from dev → staging → production.Set security gates early so unattested or vulnerable builds never make it to production.Leverage provenance attestations in JFrog Evidence for instant traceability.
What’s next
You can enable the GitHub and JFrog integration today to start building a more secure, automated, and traceable software supply chain.
For more details, check out the JFrog integration guide and the GitHub documentation.
The post How to use the GitHub and JFrog integration for secure, traceable builds from commit to production appeared first on The GitHub Blog.

